This work investigates the root causes of the lower efficiency of QLEDs utilizing organic ETLs and approaches to mitigate them. While low electron mobility has traditionally been considered the primary constraint of organic ETLs, our findings reveal that uncontrolled electron leakage toward the HTL plays a more critical role in limiting device performance. By using a multilayer ETL configuration that includes electron blocking interfaces, electron leakage can be reduced, and higher EQE can be achieved.
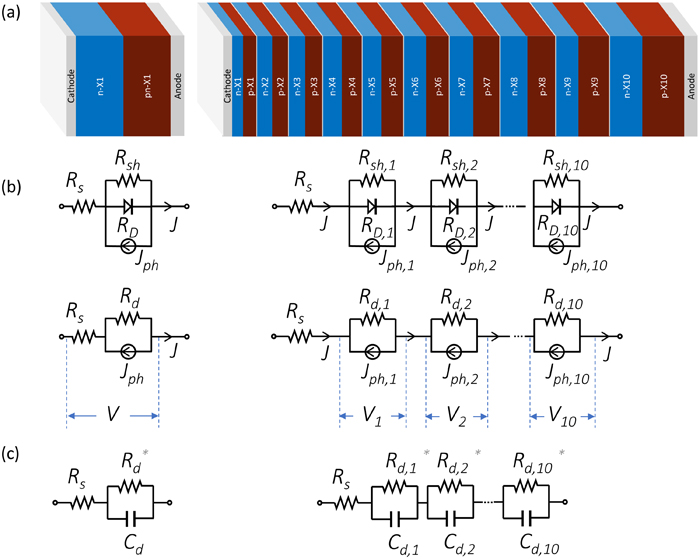
Steady-state current–voltage and impedance measurements under dark and increasing monochromatic irradiances were employed to investigate power conversion efficiency, resistance, capacitance, and quasi-open-circuit response times in single-junction (1 J) and ten-junction (10 J) In0.53Ga0.47As photonic power converters. A methodology for analyzing normalized sub-cell properties was introduced, enabling a more effective comparison between the two devices.

We have successfully developed a fully inkjet-printed flexible OPD based on TIPS-pentacene/PS for photoplethysmogram applications. The OPD showed a very low dark current of 3.14 × 10^−14 A under 5 V bias with 532 nm illumination at a light intensity of 8.2 µW cm−2, achieved a high photo-to-dark ratio (Iphoto/Idark) of 9.6 × 10^2 at the optimized channel length of 200 µm, resulting in high responsivity (R) of 0.23 A W−1, a detectivity (D*) of 1.8 × 10^11 Jones, and fast photoresponse speed of 0.22 s (rise) and 0.46 s (decay).
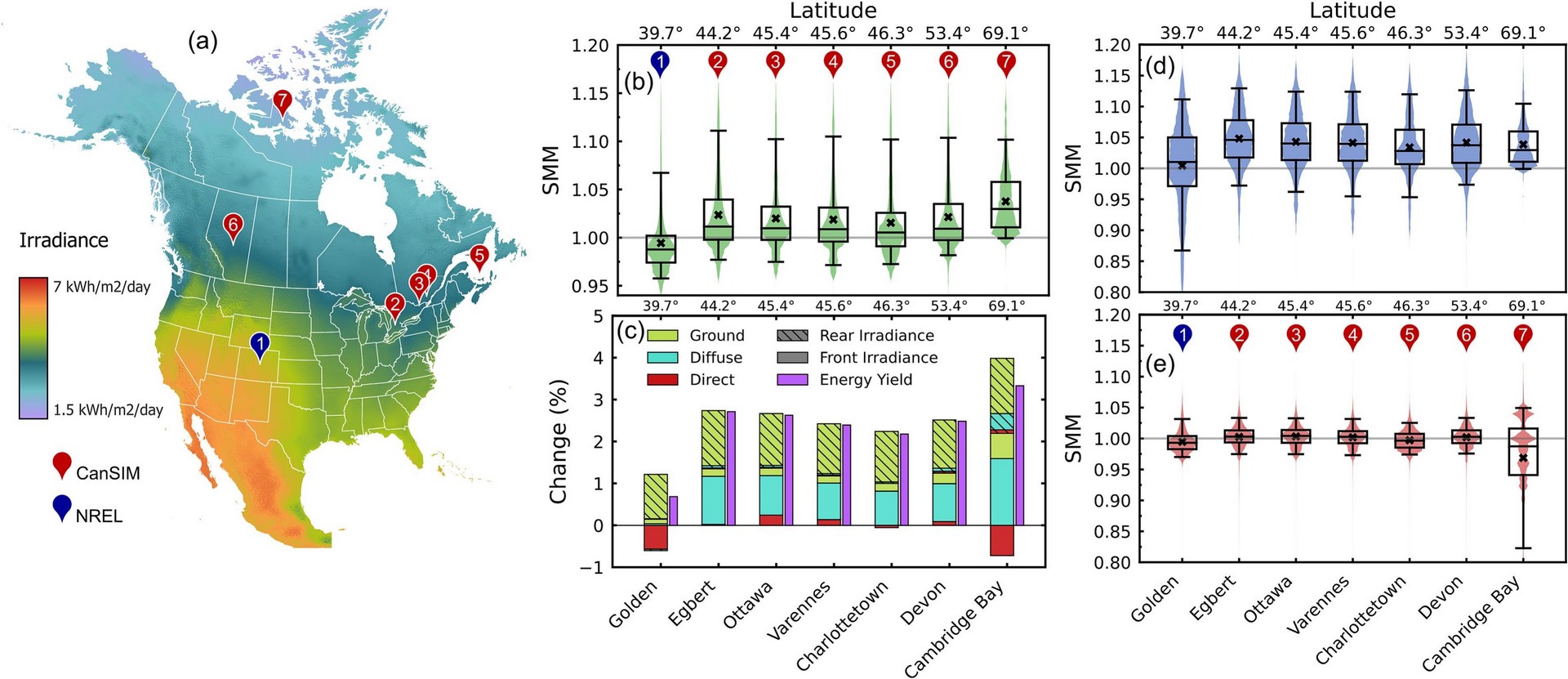
we study the importance of solar spectral irradiance for silicon bifacial PV performance prediction in seven North American locations. Bifacial energy yield is underestimated when spectral effects are neglected, primarily due to ground-reflected and diffuse light. Neglecting spectral effects can cause up to 0.6–2.7% underestimation of annual energy yield, with higher error at shorter timescales.
Three novel potassium cyclopentadienides featuring bis(dimethylamino)phosphinochalcogenoyl substituents containing sulfur, selenium, and tellurium, as well as their homoleptic complexes with EuII, were prepared and characterized. The chalcogen atom of these ligands coordinates to the lanthanide left and, in doing so, disfavours the coordination of solvent ligands. Photoluminescence studies show that the identity of the chalcogen atom has an important effect on the luminescence properties of the EuII complexes, as the emission is progressively quenched on going down the chalcogen group.
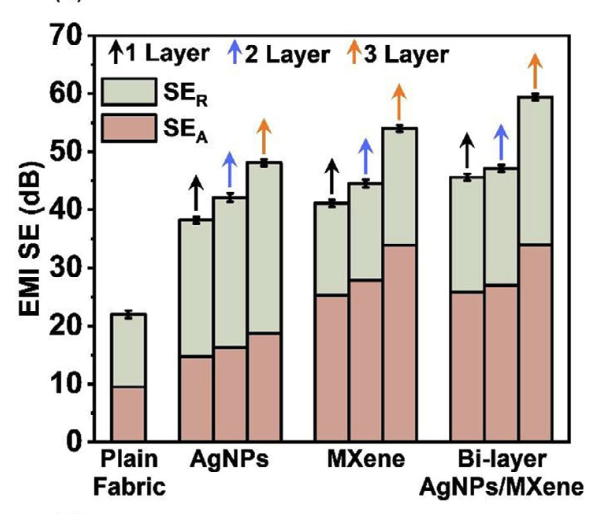
We developed a novel hybrid knitted fabric using lightweight, flexible copper-cotton core-spun yarn, functionalized with alternating bi-layer coatings of AgNPs and MXene nanosheets. The fabric exhibited an excellent EMI SE of 59.4 dB in the X-band, showcasing the strong synergistic interaction between AgNPs and MXenes.
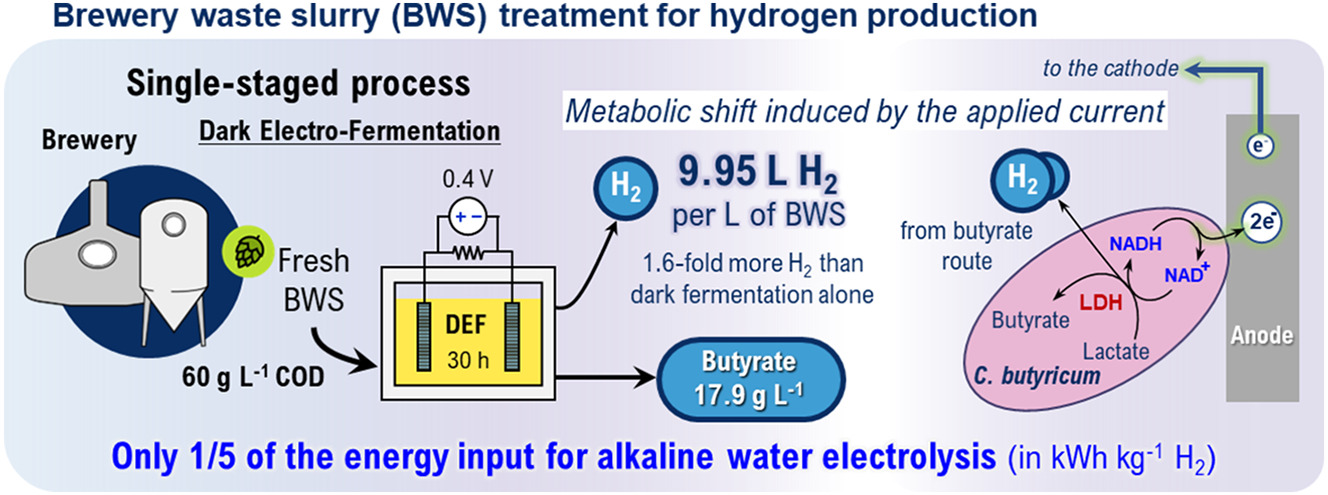
This study demonstrates that electro-fermentation is an attractive strategy to co-produce value-added chemicals and hydrogen from biomass-rich wastes like brewery waste slurries. By operating at 0.4 V, the process increased hydrogen production ~60 % compared to DF alone, accompanied by a notable butyric acid production of almost 18 g L−1.
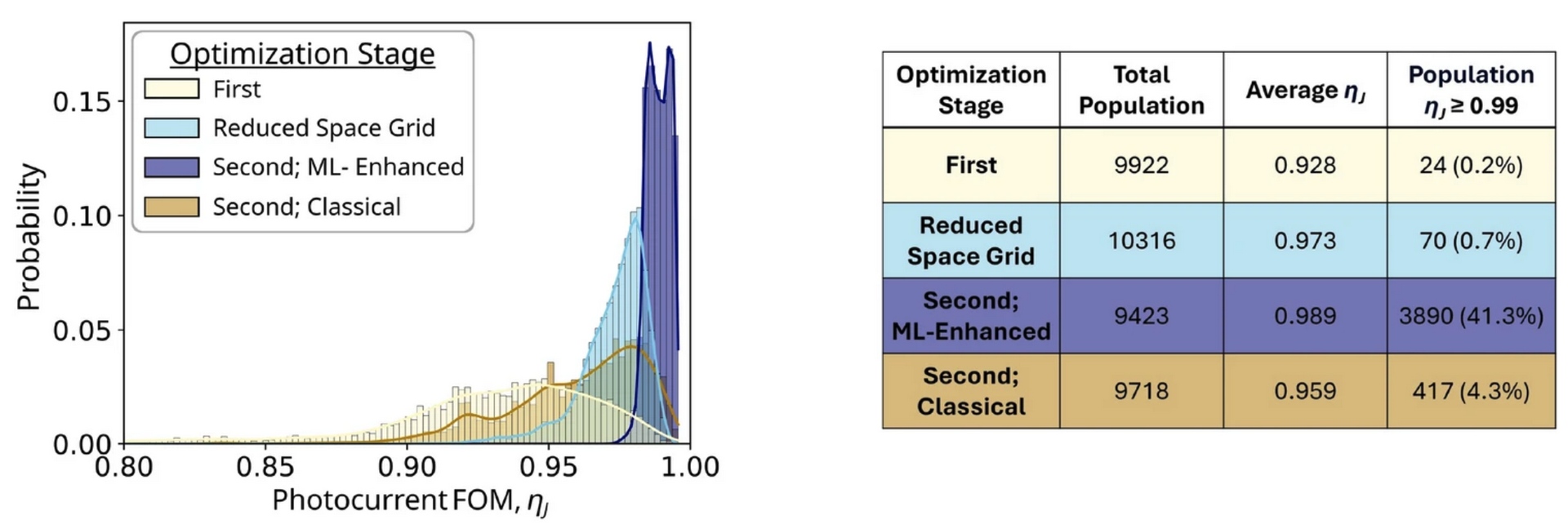
We study a ML-enhanced method which accelerates the design optimization of multi-junction PPCs. It produces a much greater number of designs attaining the highest , these have a greater design variability, and are obtained at a lower computational cost than those found using classical optimization algorithms alone. These advantages, coupled with the demonstrated knowledge discovery, exemplify an expansion in the design perspective which empowers the design choice under external constraints and preferences
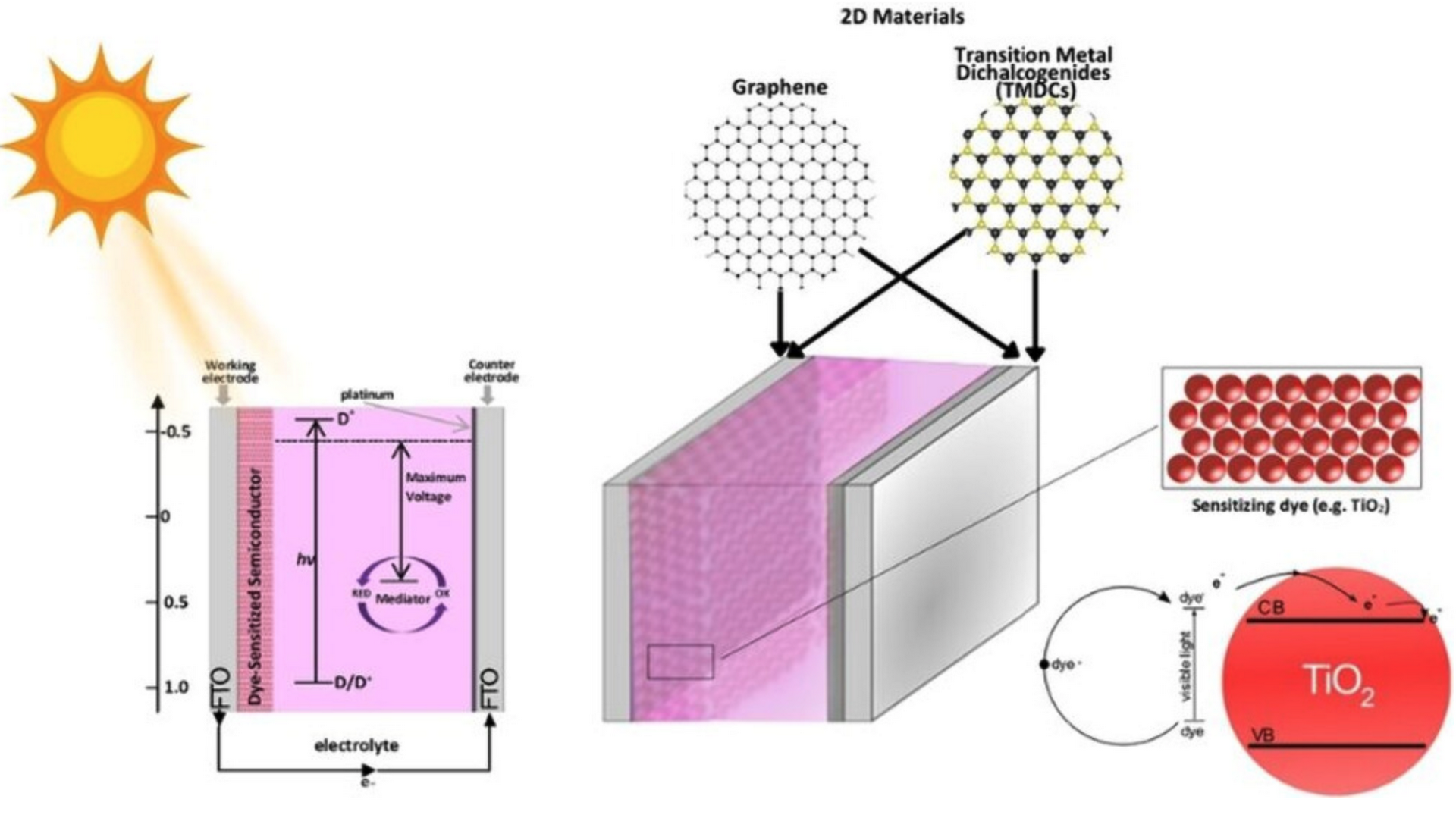
In this review, we highlight recent advances in the components of DSSCs, with a particular focus on recently published works between 2017 and 2022. The impact of COVID-19 on the research community can be seen in a drop in the number of publications in the year 2021. We will describe the development process in general terms. Special attention will be given to the advancement and use of 2D materials to increase the efficiency of working and counter electrodes.
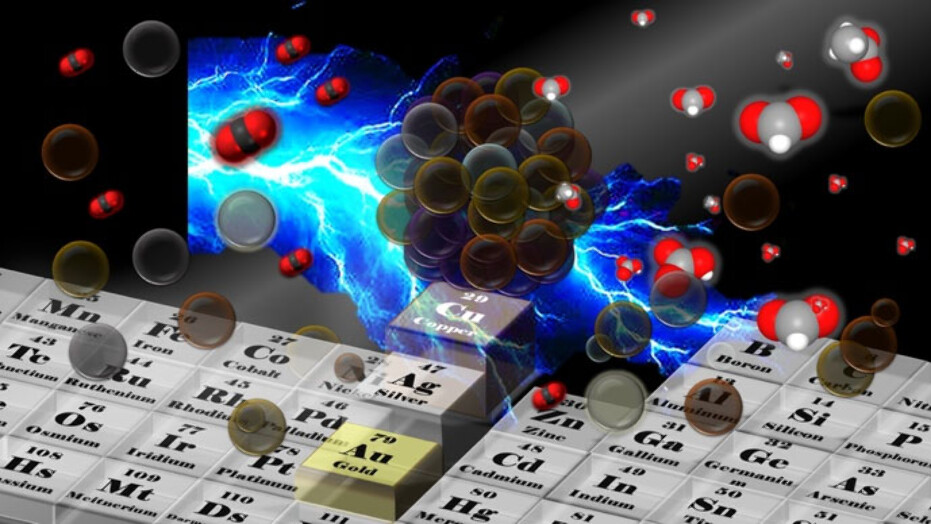
This Review highlights recent advances in plasmon-enhanced CO2ER on Au-, Ag-, and Cu-based single-metal catalysts, as well as plasmonic multi-metal catalysts. It covers experimental techniques used to elucidate plasmon-enhanced mechanisms and performance, along with in situ and computational techniques that unravel reaction mechanisms and provide a better understanding of the process.
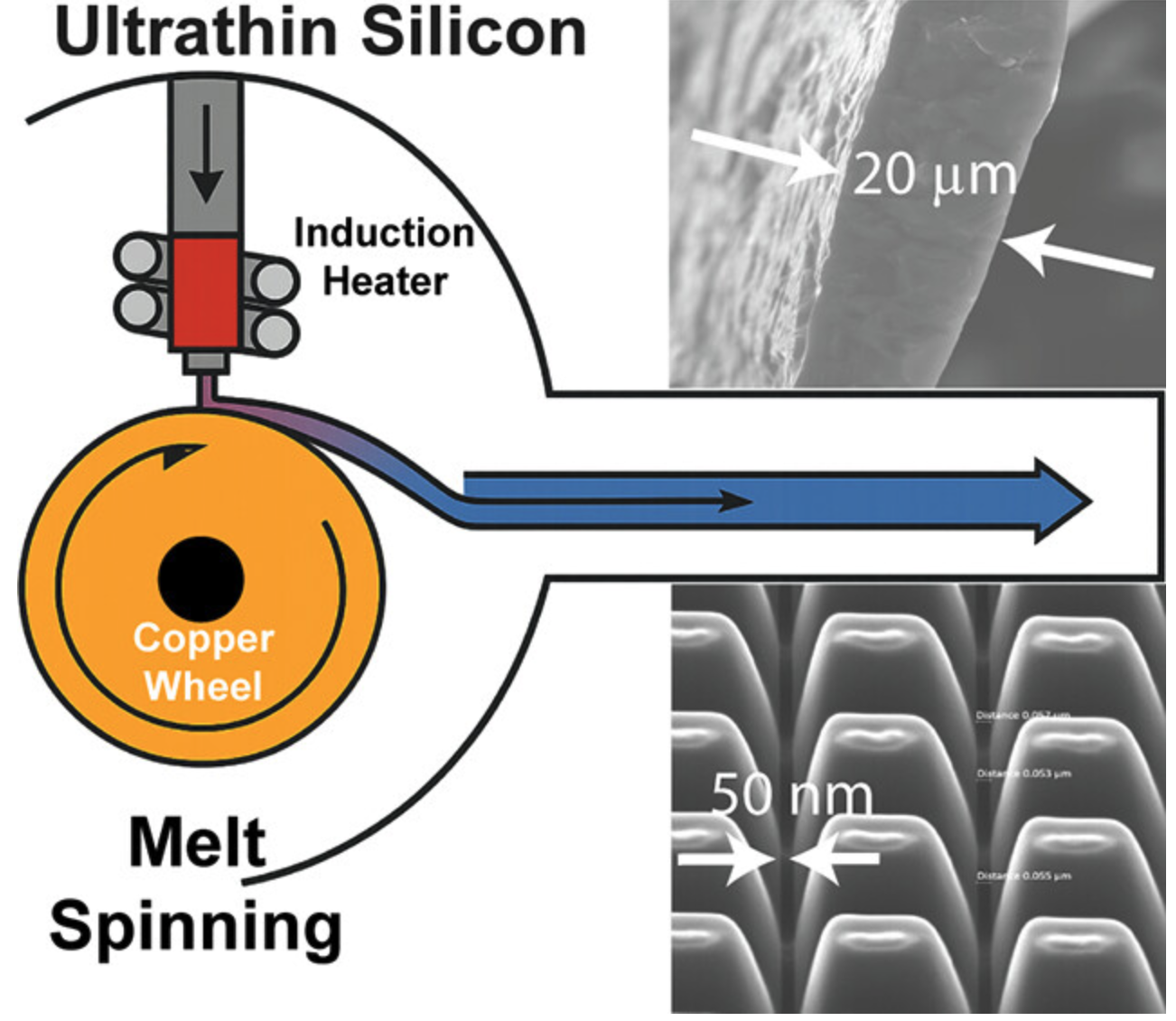
This study presents a novel method for fabricating free-standing ultrathin silicon substrates using a melt-spinning technique. By directly extruding molten silicon onto a rotating copper wheel in a controlled argon environment, we successfully fabricated polycrystalline silicon substrates with dimensions of 1 × 5 cm and a thickness below 20 μm, all within a processing window of 1 h.
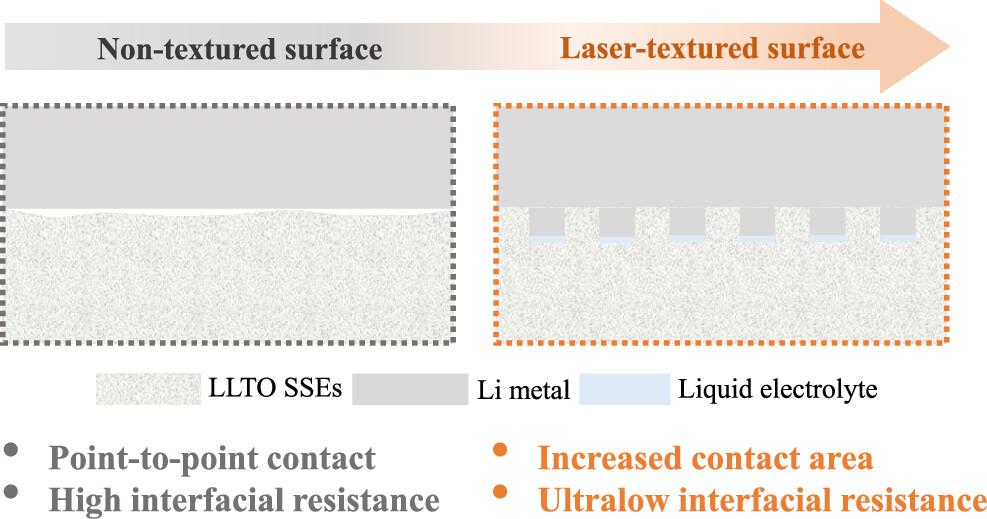
This work, for the first time, applied ultrafast-laser texturing to produce precisely controllable micropatterns onto LLTO solid-state electrolytes (SSEs). By adjustment of the laser parameters, grooves with tailored orientations and sizes can be produced onto SSE pellets. Laser processing results in a color shift related to the reduction of Ti4+ cations, as well as the formation of an amorphous layer redeposited on the sample surface.
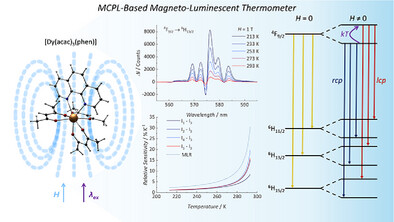
The application potential of magnetic circularly polarized luminescence (MCPL) techniques is showcased through the first demonstration of MCPL-based magneto-optical thermometry. With the presence of dual-signaled bands, and the combination of multiparametric thermal read-out with multiple linear regression, remarkable sensitivities of up to 30.6% K−1 are achieved with the [Dy(acac)3(phen)] complex at 293 K.
We show that the impurity allows probing of the wave functions of a degenerate shell on a carbon site where it is located. We confirm our predictions by a comparison with the tight-binding and ab-initio calculation as well as with experiment.

We realize surface plasmon interferometric sensors based on a multimode nanoslit used as a combiner. The phase difference in the surface plasmon waves, incident on the nanoslit, determines the resonant mode excited therein, and the radiation pattern that emerges therefrom. The device construction integrates on-chip grating couplers, gold sensing and reference surfaces, transparent claddings, sealed microfluidic channels, and a nanoslit in the gold film.
We improve and simplify the design and characterization processes for photonic power converters, exceeding 50% efficiency under 1.446 μm laser light. We develop a calibrated model predicting efficiency gains with increasing bandgap, reaching up to 57% efficiency at a 1.3-μm wavelength.
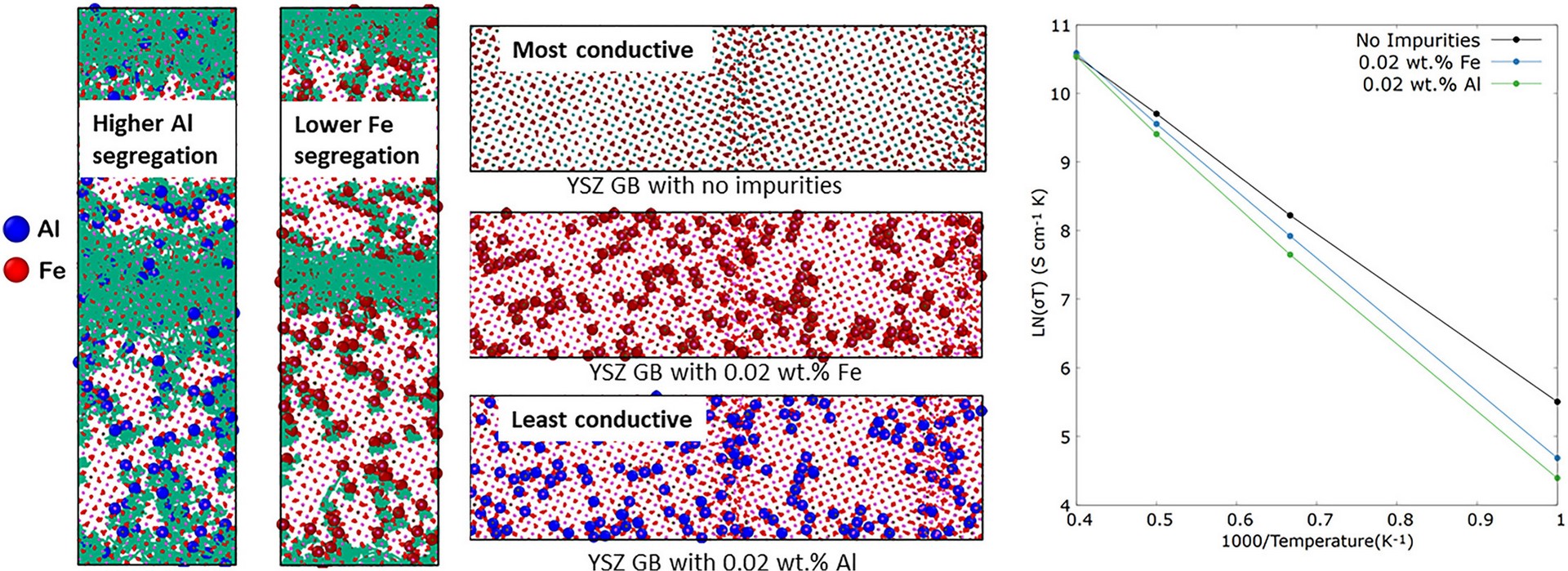
The present work systematically investigates segregation behaviors of aluminum (Al) and iron (Fe) impurities in YSZ grain boundaries by using molecular dynamics simulations. We have investigated the dynamics of Al and Fe impurities across two grain boundary configurations, symmetric and mixed boundaries, with respect to their relative impacts on oxygen ionic conductivity.
The laser ablated craters were analysed with Raman spectroscopy and reveal the formation of Ag2O and AgO at different pulse energies and number of pulses. A mechanistic picture for the formation of both silver oxides and their transformation into Ag2CO3, Ag2SO3 and Ag2SO4 is proposed. Some laser-induced periodic surface structures LIPSSs were also observed on some craters, as well as nanoparticles arranged in concentric patterns.
We introduced Ag, Au, Co, Fe, Ru, Pd, and Pt single-atom dopants to enhance the catalytic performance of the Cu0.5Ni0.5(111) surface. Using rigorous DFT calculations, we evaluated catalyst stability, N2 and H2 activity, and the rate-limiting steps of the NRR
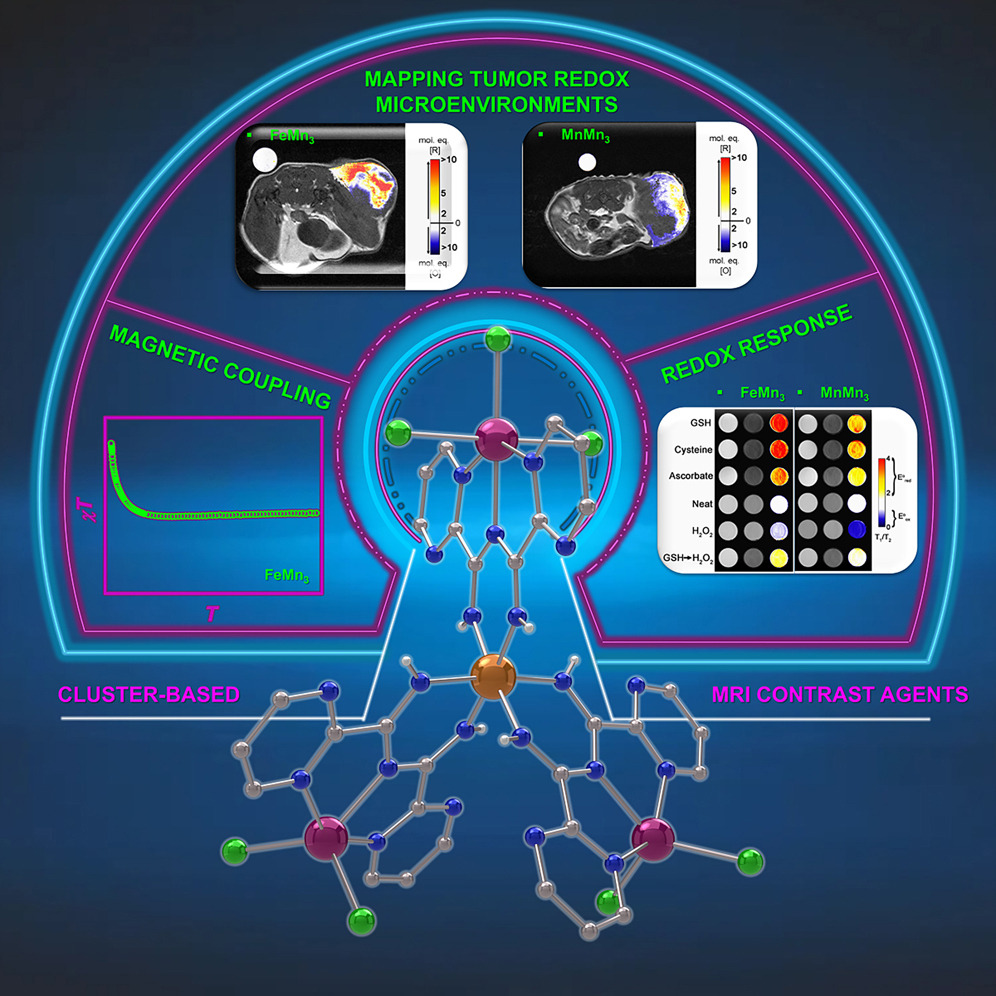
Transition metal molecular clusters hold great promise as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) probes, where careful chemical design can afford control over the size, shape, and total spin state of the contrast agent (CA). Although such clusters can act as a single entity, exhibiting advanced in situ reactivity to key diagnostic biomolecules, their dissociation/speciation in biological media hinders their potential as MRI CAs. To resolve this, the N-2-pyrimidylimidoyl-2-pyrimidylamidine chelate was employed to selectively bind 3d metal ions, forming highly stable mixed-metal clusters.
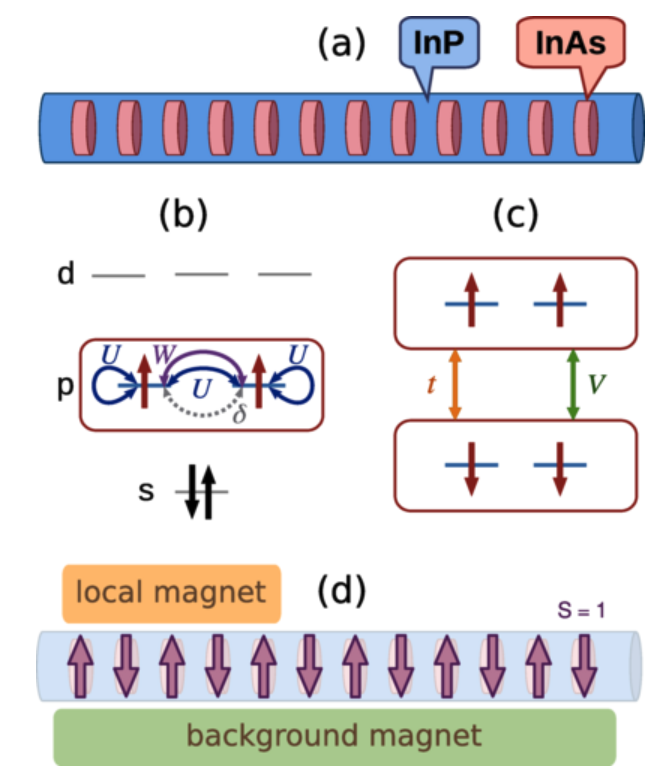
we investigated the coupling of two singlet-triplet Haldane (STH) qubits realized in a quantum dot nanowire with four electrons in each dot through a gated control dot. By computing the energy spectrum of the fermionic system, we demonstrated that each quantum dot nanowire behaves like a topological Haldane chain with Haldane quasiparticles at both ends.
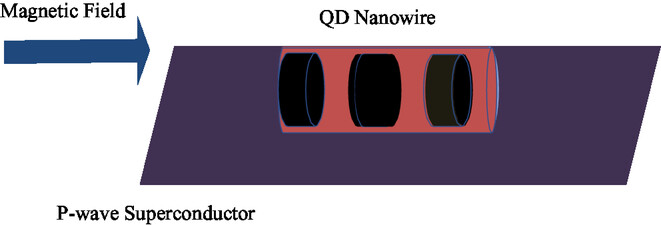
We presented steps toward designing Majorana Quasiparticles in InAsP QD in InP Nanowires on p-wave superconductor with QNANO and variational quantum eigenvalue (VQE) solver on a quantum computer. We used VQE approach to estimate the ground state energy of the seminconducting QD nanowire in the proximity of a p-wave superconductor, in the presence of applied external magnetic field, described by the Kitaev chain.
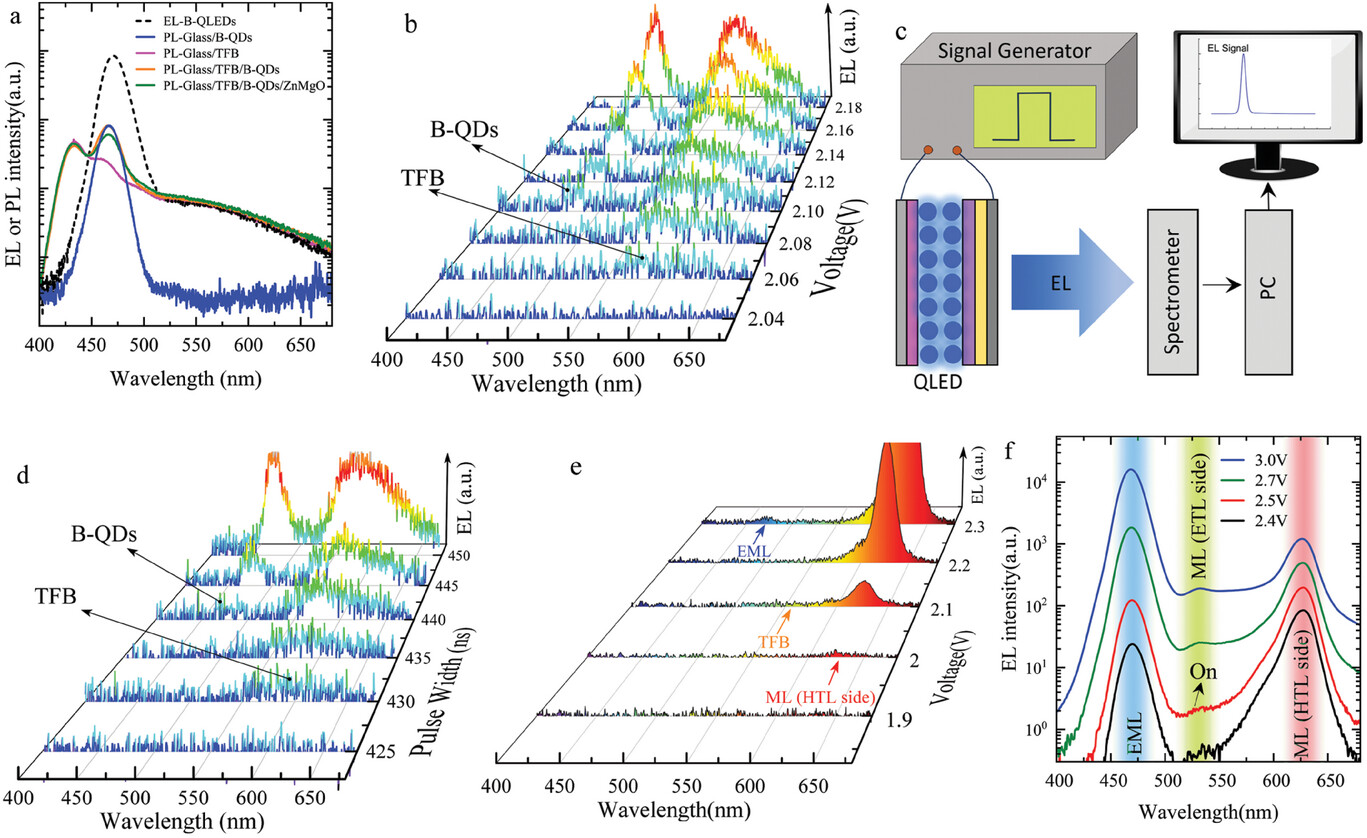
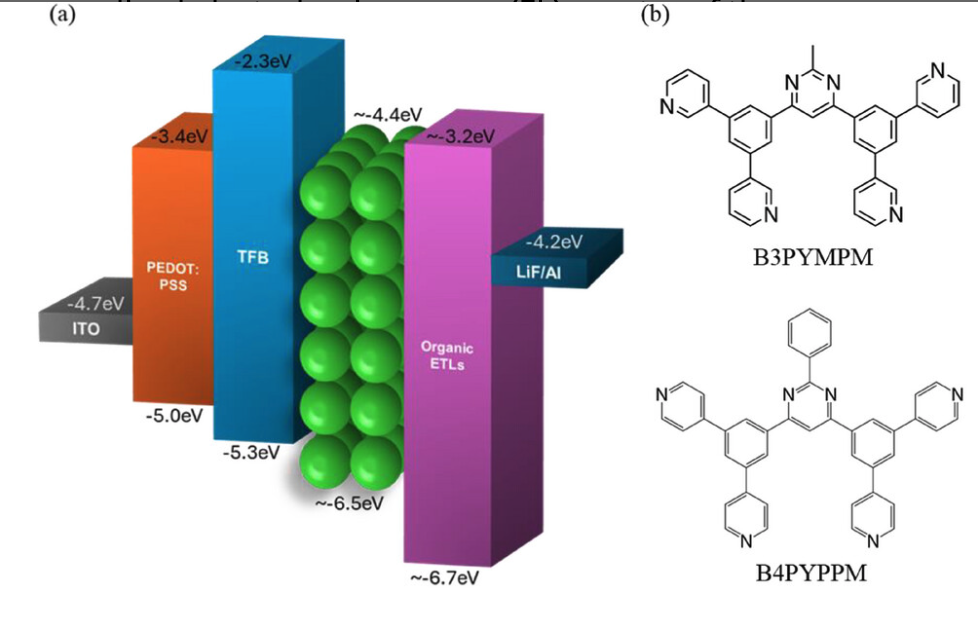
An increase in electron leakage and electron-induced damage to the hole injection layer (HIL) that leads to a deterioration in hole supply are found to play a key role in the rapid EL loss in B-QLEDs. EL and PL measurements on B-QLEDs, fabricated with and without luminescent MLs, show that the electron supply is easier than the hole supply, resulting in an electron e/h ratio >1 in the B-QDs-EML and significant electron leakage into the HTL and to the HIL.
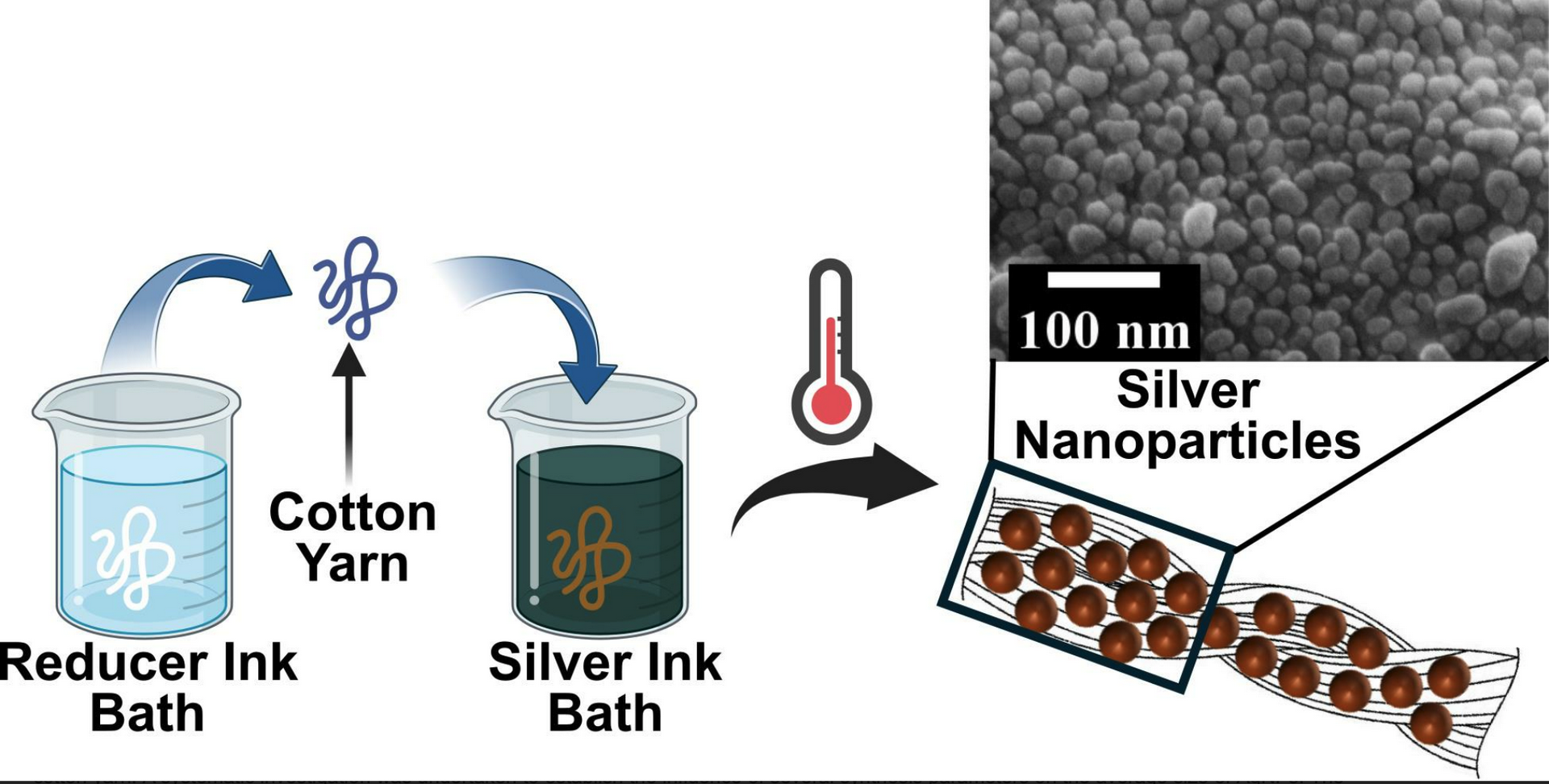
We have successfully developed a scalable method for impregnating cotton yarn with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs), presenting a cost-effective approach with potential applications in functional coatings, wearable electronics, biomedical applications, and smart textiles. Our study highlights several critical parameters that influence the growth and average size of AgNPs during their in situ synthesis on cotton yarn.
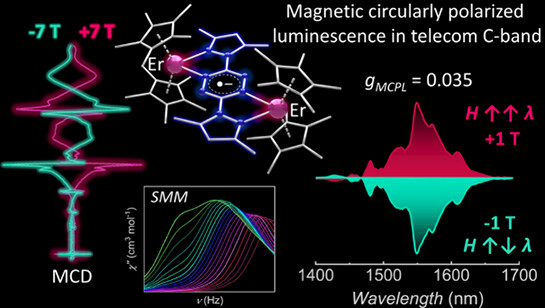
The magnetic and magneto-optical properties of a tetrazinyl radical-bridged ErIII metallocene, [(Cp*2ErIII)2(bpytz•–)][BPh4] (1; Cp* = pentamethylcyclopentadienyl, bpytz = 3,6-bis(3,5-dimethyl-pyrazolyl)-1,2,4,5-tetrazine), are reported.
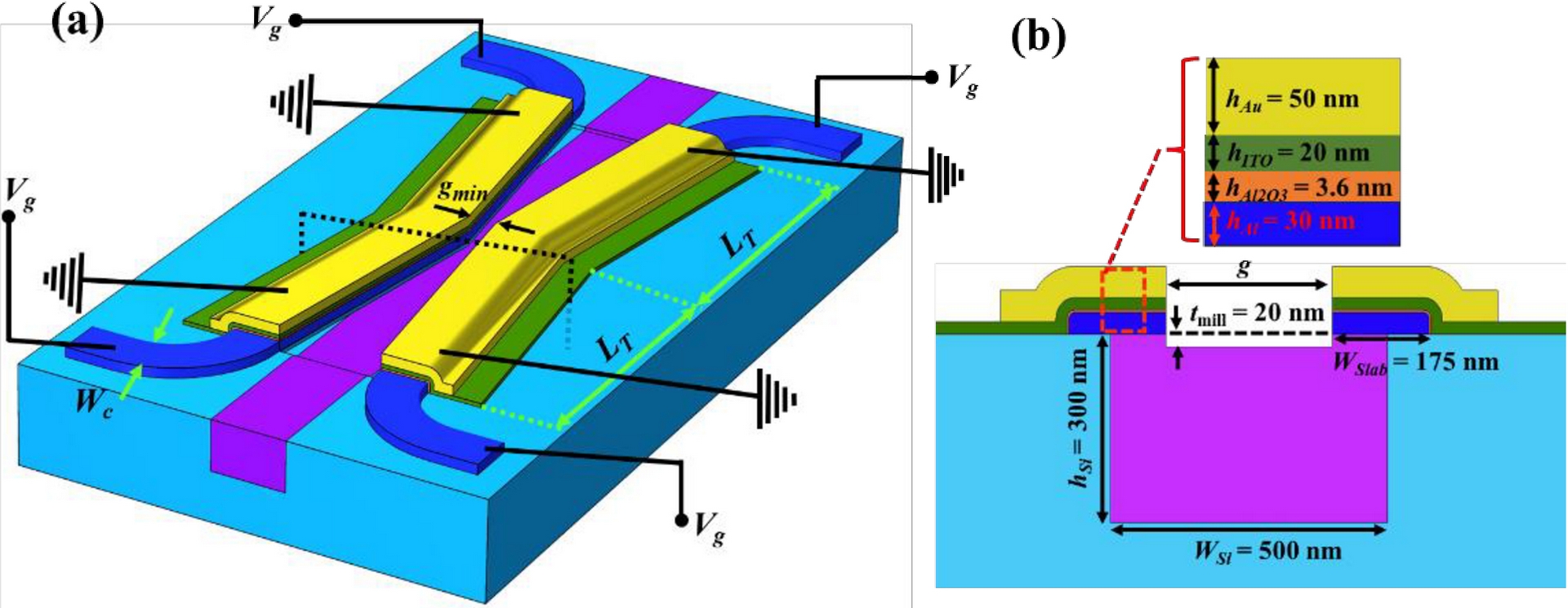
By combining the nanoscale field confinement of surface plasmon polaritons with the ENZ effect, our modulators, integrated with silicon waveguides and optimized for operation at λ = 1550 nm, achieve a 3-dB bandwidth of 210 GHz, an insertion loss of 3 dB, and an extinction ratio of 5 dB for a device length of under 4 µm.
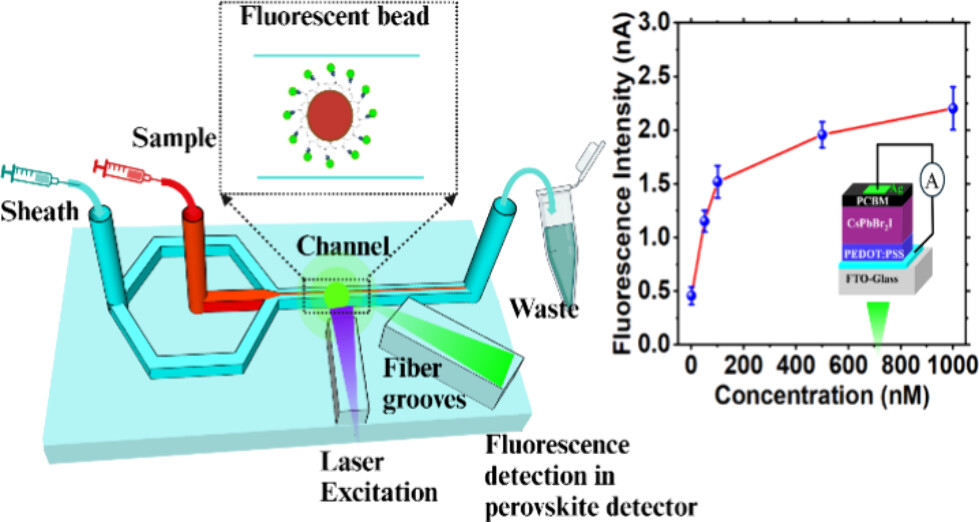
We have demonstrated the potential of the CsPbBr2I perovskite-based photodetector for self-powered operation and optofluidic integration. By harnessing the controlled light-induced poling phenomenon, an electric field was induced within the perovskite material, eliminating the stability and degradation issues associated with traditional electrical poling methods.
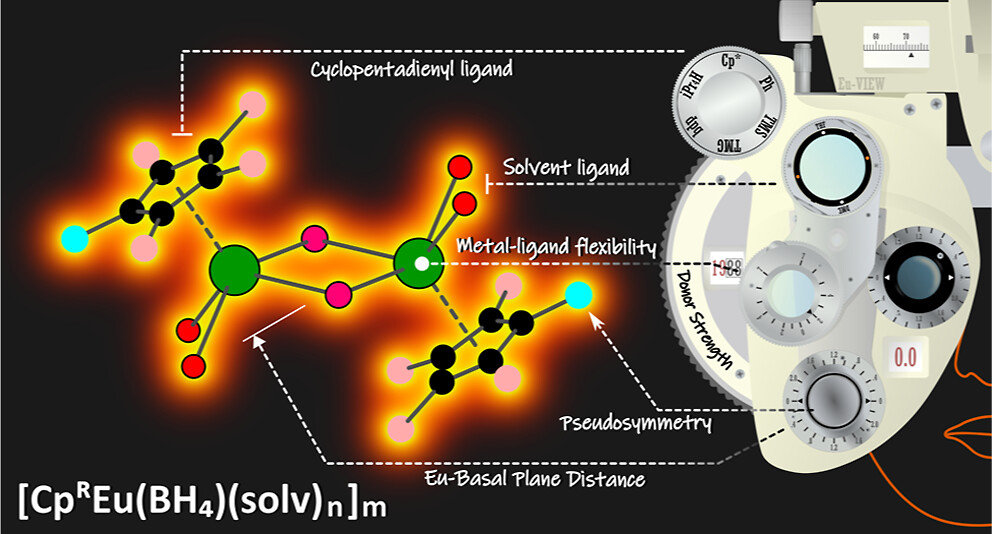
This study demonstrates that thermochromic emission is an intrinsic property of EuIIhemimetallocenes and highlights the complex interactions that give rise to this property and the challenges in elucidating and disambiguating their influence. We expect that the insights gained herein will aid in driving and directing the development of increasingly advanced molecular optical materials based on EuII, with finely tunable photophysical characteristics.
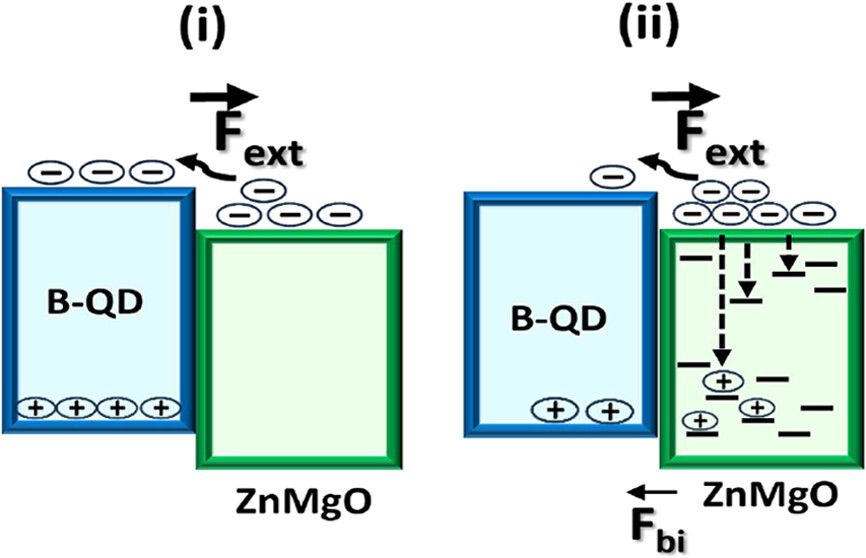
This study reveals that hole leakage into the ZnMgO ETL can be significant in B-QLEDs and can have adverse effects on it. PL and electrical measurements on electron-rich and hole-rich devices show that holes damage the ZnMgO layer by developing sub-band gap states in the ETL.

This review comprehensively examines the integration of advanced plasmonic materials in PCF biosensors, highlighting significant advancements and potential future directions in biosensing technology. Through the lens of recent developments in materials science and optical engineering, it explores how graphene, transition metal dichalcogenides, black phosphorus, silicon, and germanium enhance the performance of PCF biosensors, offering improved sensitivity, specificity, and label-free detection capabilities.
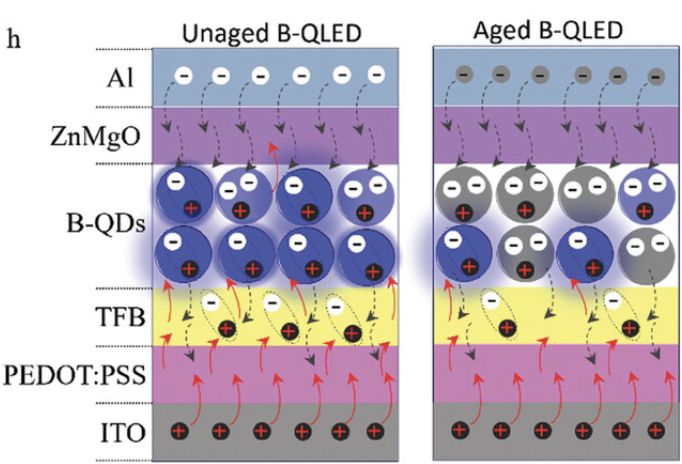
An increase in electron leakage and electron-induced damage to the hole injection layer (HIL) that leads to a deterioration in hole supply are found to play a key role in the rapid EL loss in B-QLEDs. EL and PL measurements on B-QLEDs, fabricated with and without luminescent MLs, show that the electron supply is easier than the hole supply, resulting in an electron e/h ratio >1 in the B-QDs-EML and significant electron leakage into the HTL and to the HIL. Under electrical stress, electron leakage increases, and hole supply deteriorates further causing charge imbalance to increase, and, as a result, the EQE decreases.
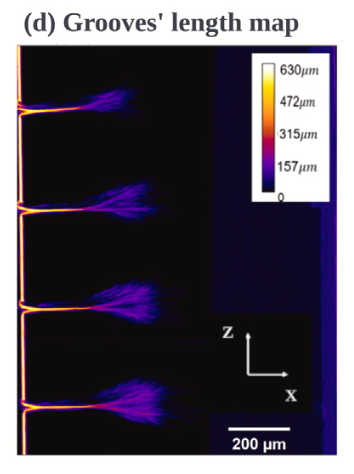
Ultrafast laser machining has been researched extensively over the last few decades to create features such as holes in a variety of materials. The effects of laser parameters including power and polarization on the dynamics of hole formation and resulting hole geometry have been studied.
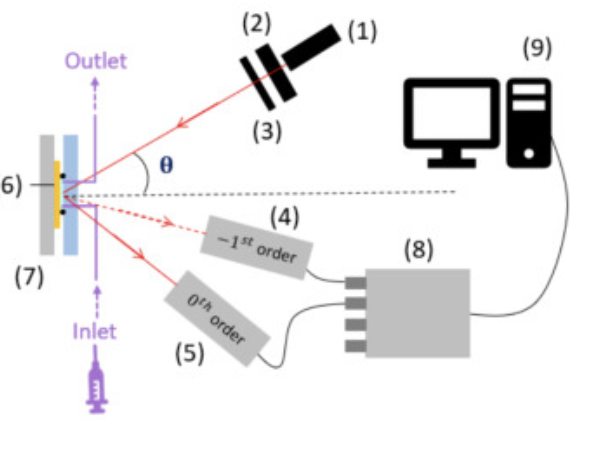
A deep gold-coated sinusoidal grating is proposed as a transducer for label-free real-time biosensing, operating in a new configuration based on the optical switch effect, which produces complementary optical outputs enabling differential and referenced detection.
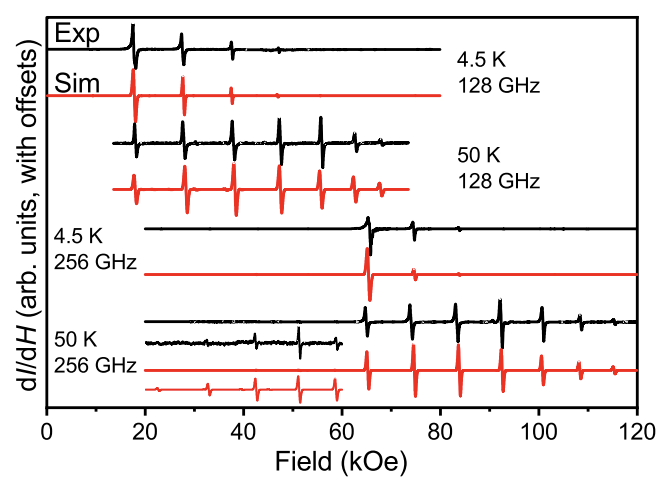
Single-ion anisotropy is vital for the observation of Single-Molecule Magnet (SMM) properties (i.e., a slow dynamics of the magnetization) in lanthanidebased systems. In the case of europium, the occurrence of this phenomenon has been inhibited by the spin and orbital quantum numbers that give way to J = 0 in the trivalent state and the half-filled population of the 4f orbitals in the divalent state.
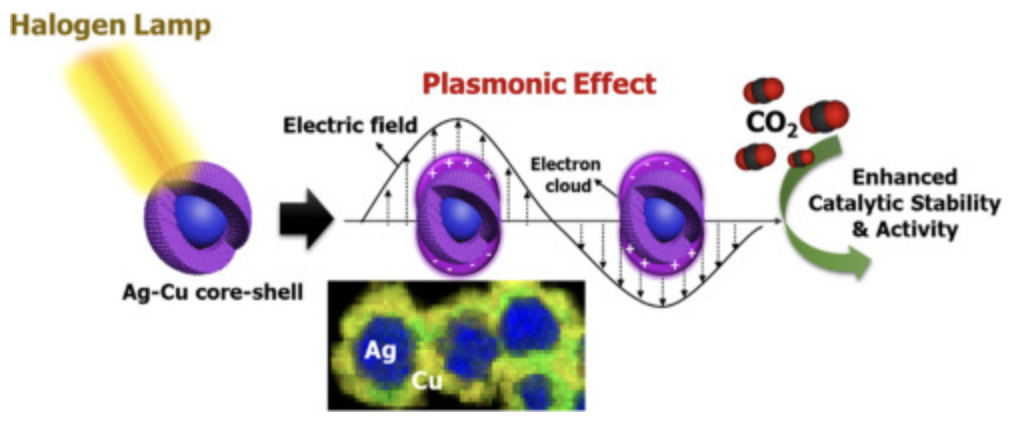
CO2 electrochemical reduction (CO2ER) allows the conversion of CO2 into fuels and chemicals. Copper is the only known catalyst that converts CO2 into hydrocarbon products but is hindered poor selectivity and stability. Cu-based bimetallic particles have shown to improve the selectivity and stability of the catalysts.
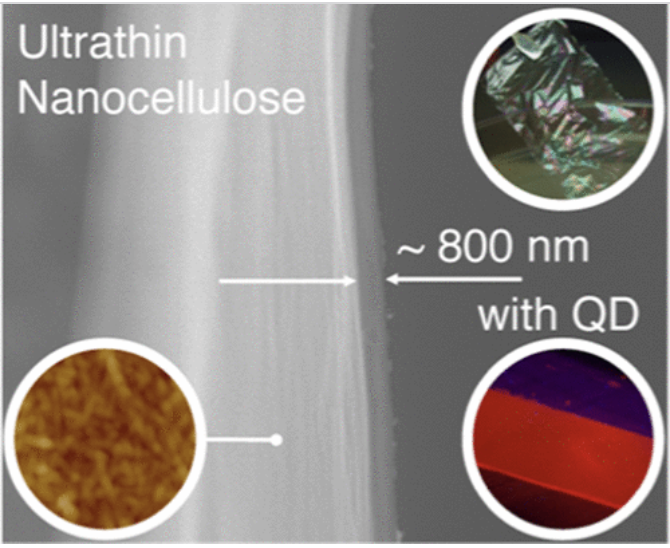
This paper presents a versatile method to fabricate ultrathin nanofibrillated cellulose (NFC) films as thin as 800 nm by blade coating, which is compatible with a roll-to-roll process on a large scale.
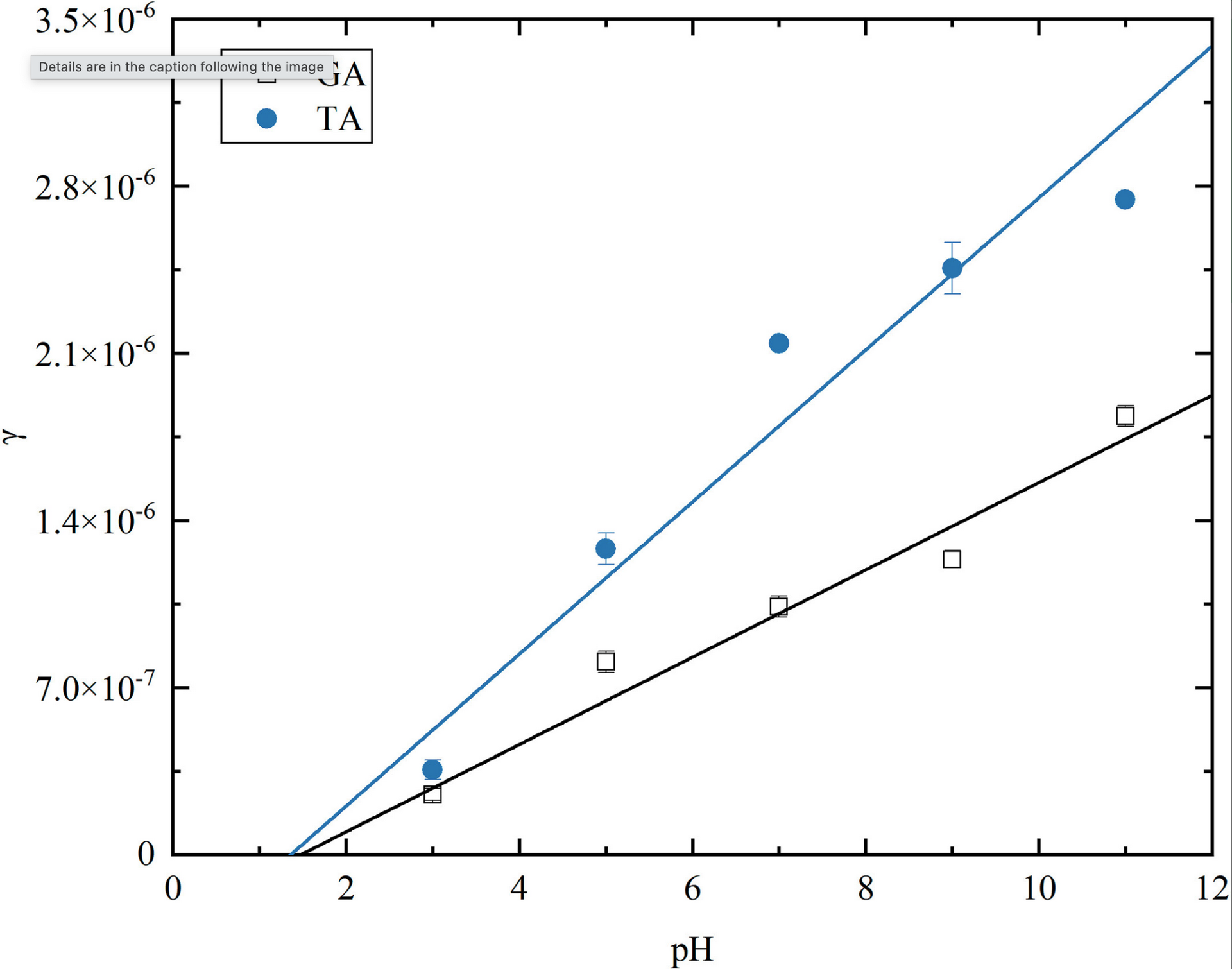
Humic-like substances (HULIS) are a ubiquitous reactive component of atmospheric aerosol. They participate in the formation of secondary organic aerosols via chemical reactions with atmospheric oxidants. Here, we assess the influence of transition metal ions (namely ferric iron, Fe(III)), and nitrate ions (NO3−) on the heterogeneous reaction of gaseous NO2 with an aqueous film containing gallic acid (GA) or tannic acid (TA) as proxies for HULIS.
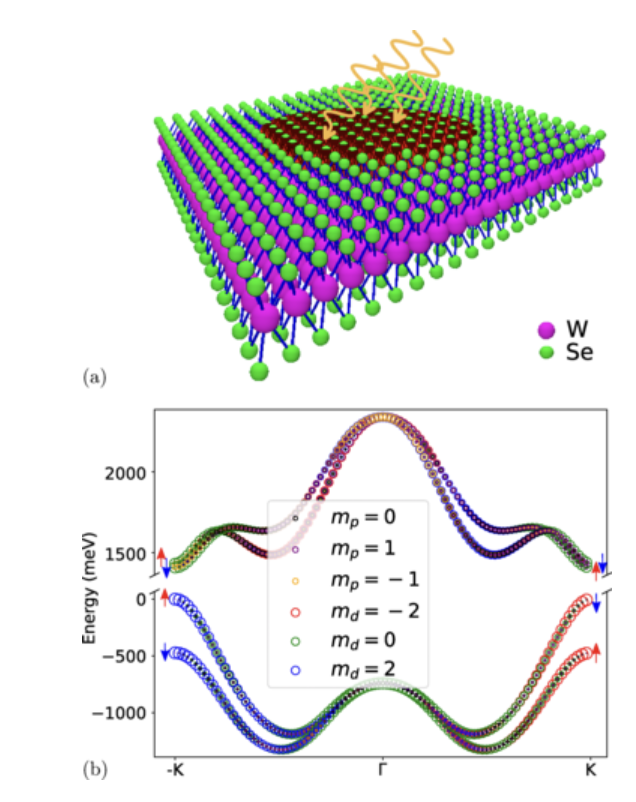
We present here a theory of excitonic complexes in gated WSe2 quantum dots (QDs). The QD gate potential causes type-II band alignment, i.e., electrostatically confines holes and repels electrons, or vice versa. Hence, the confinement of excitons involves a delicate balance of the repulsion of electrons by the gate potential with the attraction by the Coulomb potential of the hole localized in the QD.
2D materials with high charge carrier mobility and tunable electronic band gaps have attracted intense research effort for their potential use as active components in nanoelectronics. 2D -conjugated polymers (2DCP) constitute a promising sub-class due to the fact that the electronic band structure can be manipulated by varying the molecular building blocks, while at the same time preserving the key features of 2D materials such as Dirac cones and high charge mobility.
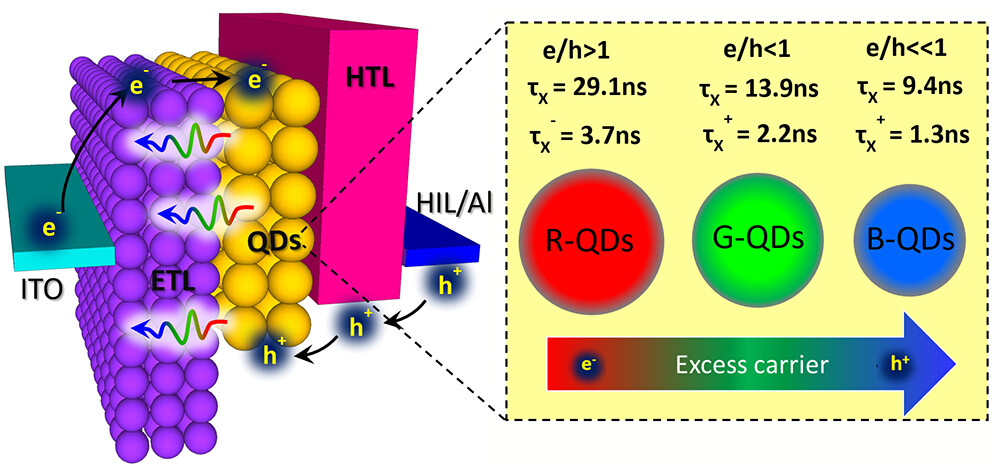
Comparative systematic investigations of inverted R-, G-, and B-QLEDs reveal significant differences in electron and hole injections among the three colors, resulting in significant differences in e/h ratios and charge balance among them. In general, R-QLEDs have electrons as excess carriers (i.e., e/h > 1) in their EMLs, whereas in both G- and B-QLEDs, the EMLs generally have excess holes (i.e., e/h < 1) with charge balance conditions being significantly worse in the case of B-QLEDs (i.e., e/h ≪ 1).
The decline in freshwater availability has spurred research into employing solar desalination technology. Recent research has concentrated on investigating the use of surface modification to improve the productivity of solar still for desalination.
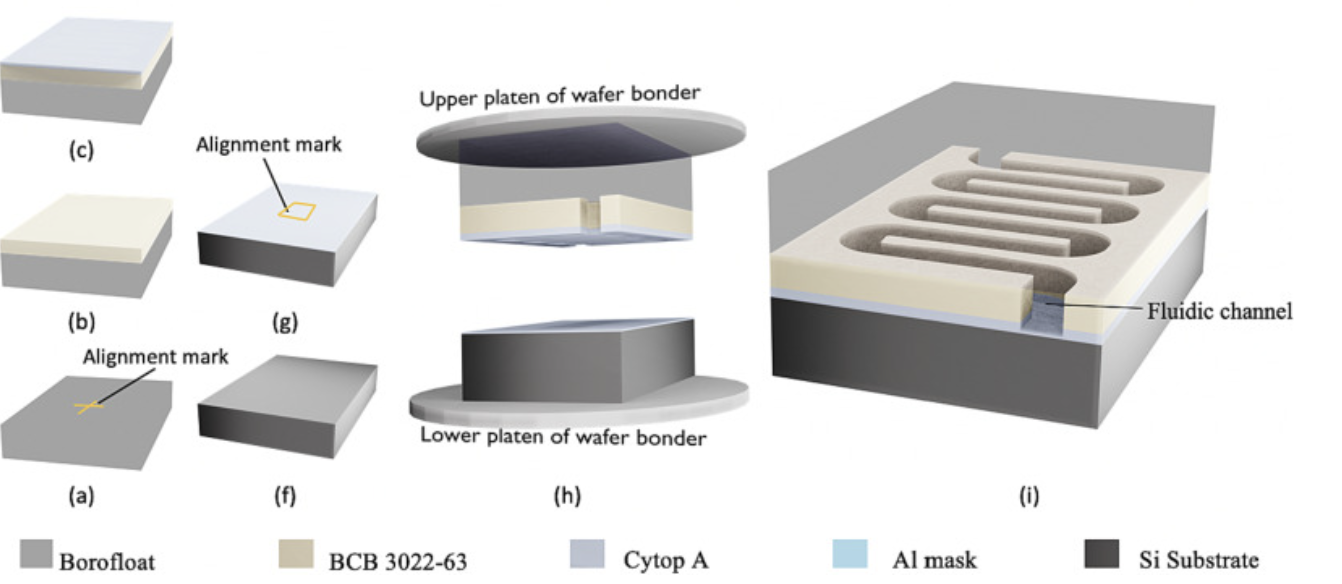
The wafer-scale fabrication of deep channel microfluidics for lab-on-a-chip applications by reactive ion etching and wafer bonding is reported. The microfluidic channels are etched in B-stage bisbenzocyclobutene (BCB) and Cytop with the latter used as a bonding agent.
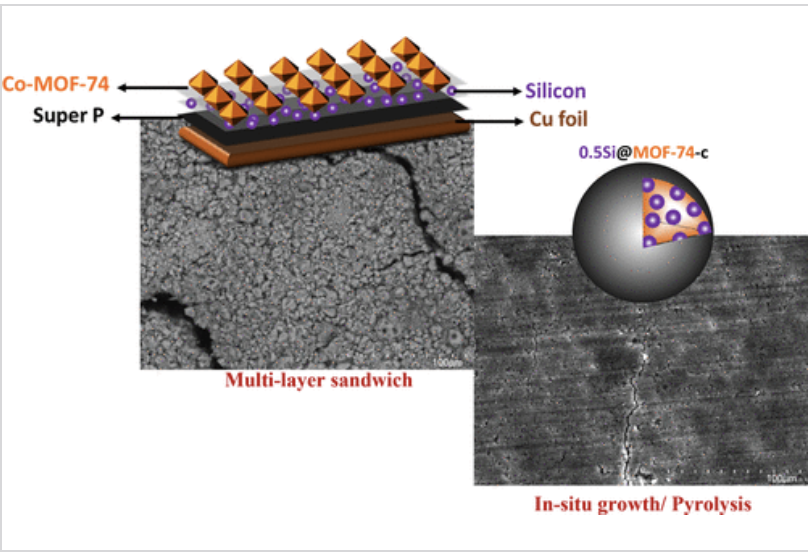
The poor capacity retention of the silicon (Si) anode has hindered its widespread use in lithium-ion batteries. Metal–organic-frameworks (MOF) may offer the structural and functional tunability needed to alleviate some of the longstanding problems associated with silicon pulverization.
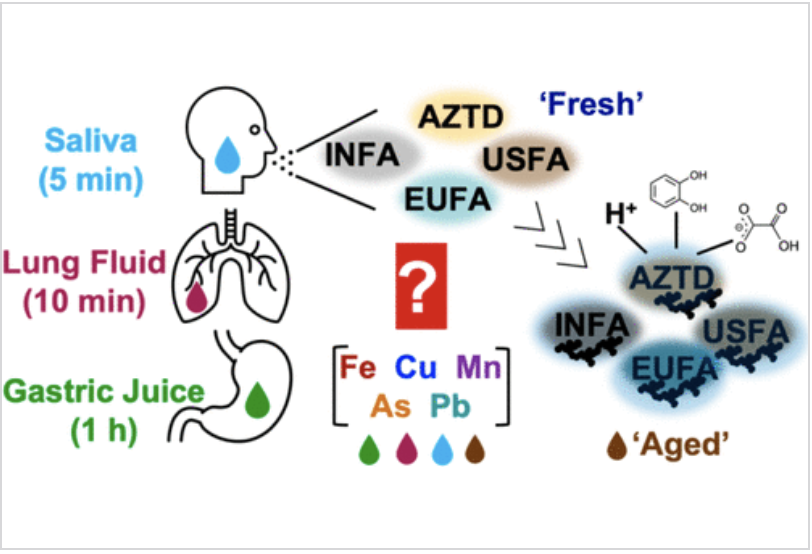
Here, we use fully characterized reference solid materials, namely, Arizona test dust (AZTD) and combustion coal fly ash samples from India, the U.S., and Europe, representative of atmospheric aerosol particles from natural and combustion sources. Using ICP-MS and optimized analytical procedures that address technical challenges with selectivity and sensitivity, we quantified the concentrations of dissolved TE Fe, Cu, Mn, As, and Pb under simulated atmospheric aging.
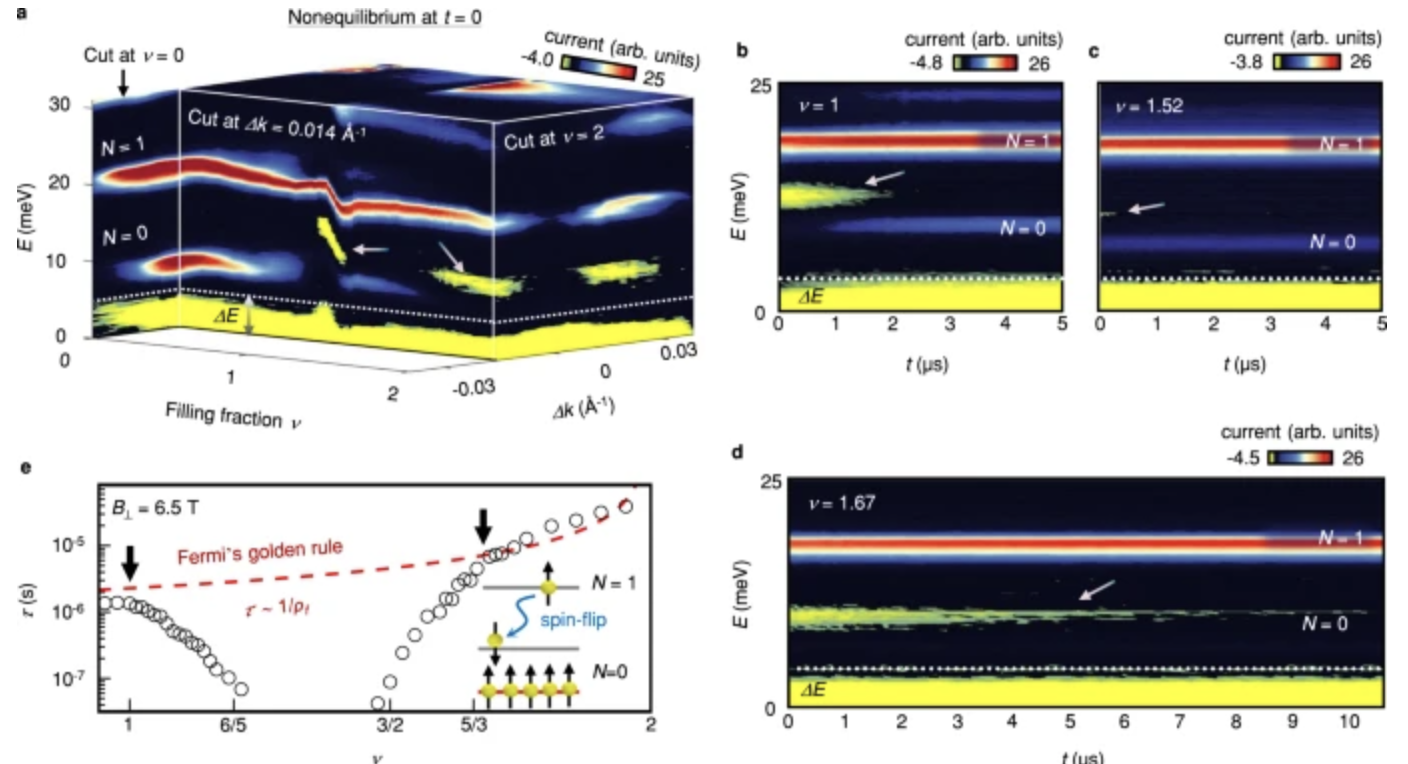
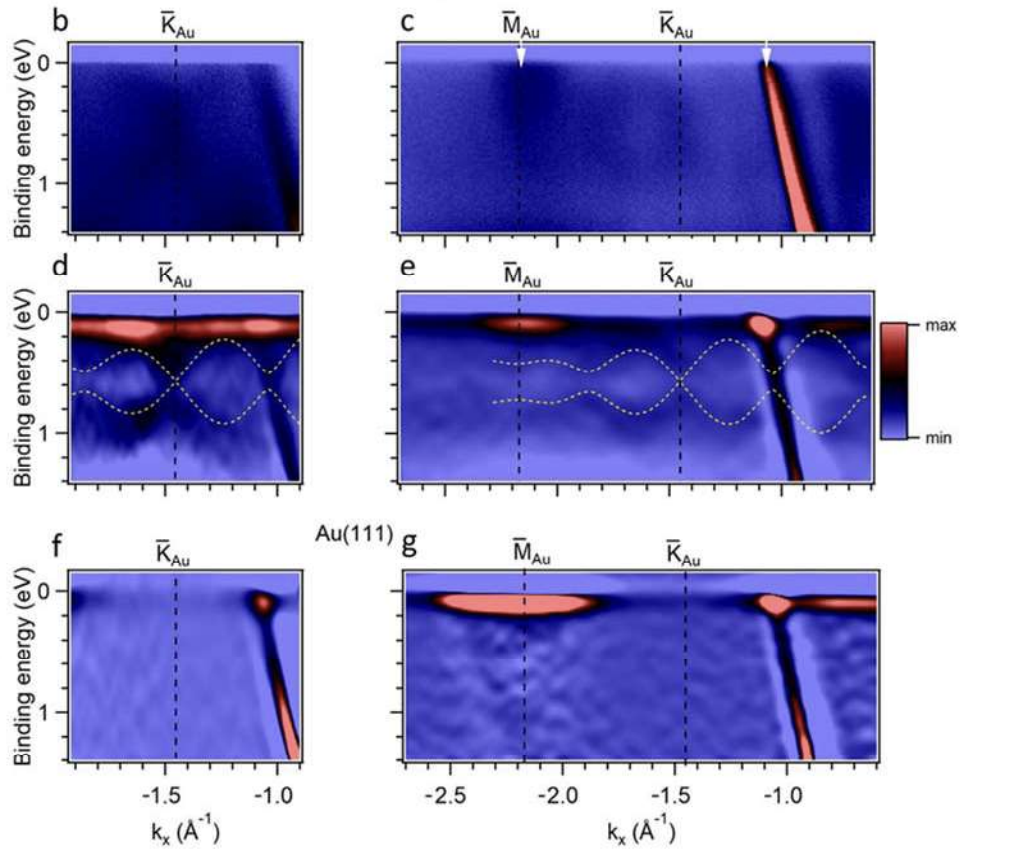
Real-time probing of electrons can uncover intricate relaxation mechanisms and many-body interactions in strongly correlated materials. Here, we introduce time, momentum, and energy resolved pump-probe tunneling spectroscopy (Tr-MERTS). The method allows the injection of electrons at a particular energy and observation of their subsequent decay in energy-momentum space.
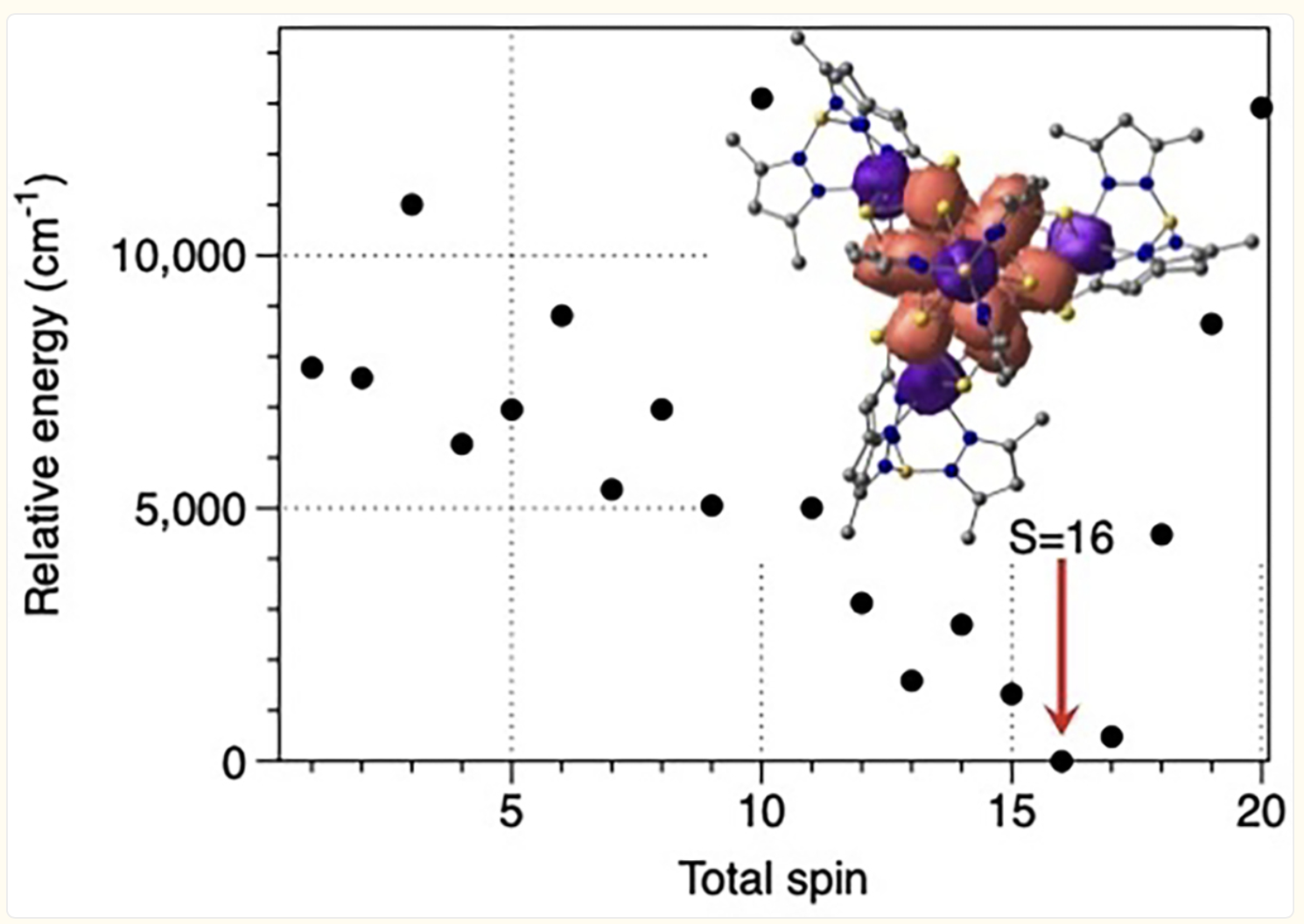
Atomically defined large metal clusters have applications in new reaction development and preparation of materials with tailored properties. Expanding the synthetic toolbox for reactive high nuclearity metal complexes, we report a new class of Fe clusters, Tp*4W4Fe13S12, displaying a Fe13 core with M–M bonds that has precedent only in main group and late metal chemistry.
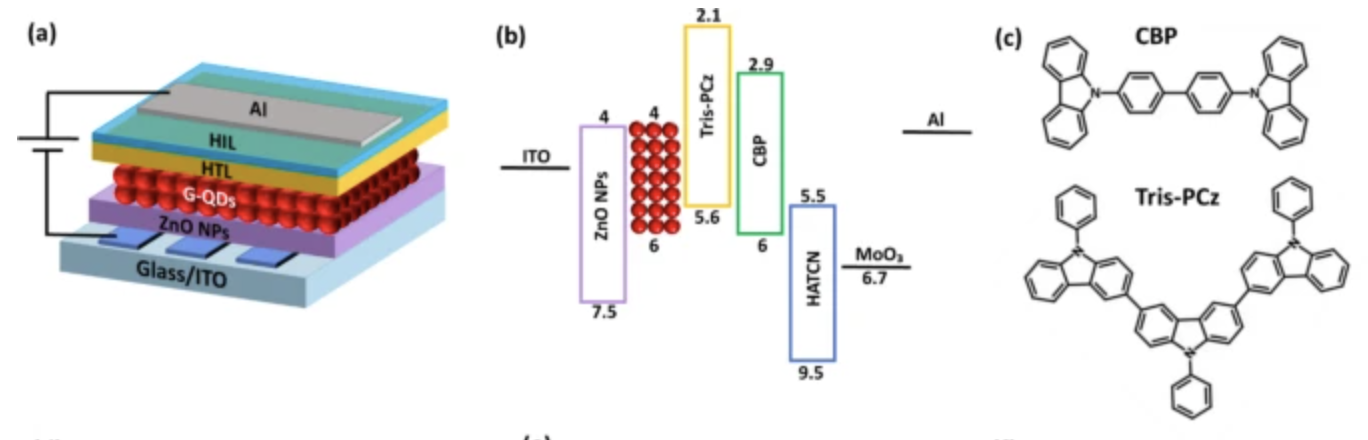
This study investigates the impact of an engineered hole transport layer (HTL) on the stability of electroluminescent quantum dot light-emitting devices (QDLEDs). The 9-Phenyl-3,6-bis(9-phenyl-9Hcarbazol-3-yl)-9H-carbazole (Tris-PCz) HTL, which possesses a shallower lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO) energy level compared to the widely used 4,4′-bis(N-carbazolyl)-1,1′-biphenyl (CBP) HTL, is employed to confine electron overflow toward the HTL.
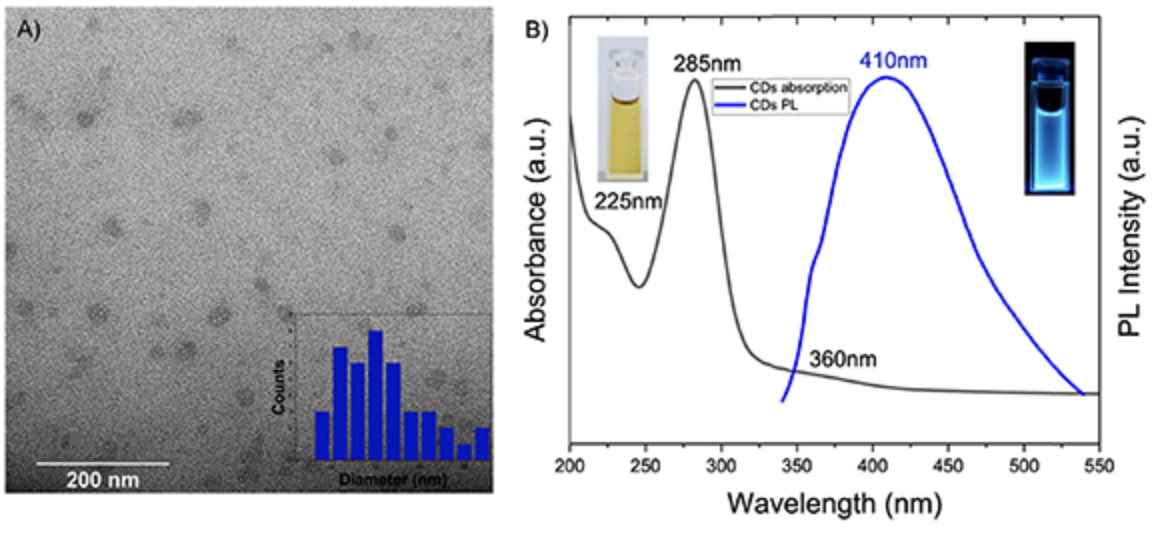
The use of sustainable materials in high-tech devices is one way to decrease the carbon footprint and tackle global climate change. We first synthesized blue-emissive carbon dots (CDs) from biocompatible onion inner epidermal cells using solvothermal method. Then, cellulose nanofiber was prepared by TEMPO oxidization, followed by homogenization from soft wood source.
Bilayer borophene, predicted to be stabilized by interlayer linkages, has now been grown by molecular beam epitaxy on copper and silver surfaces in two independent studies. The growth substrate and temperature are found to influence the lattice structures formed.
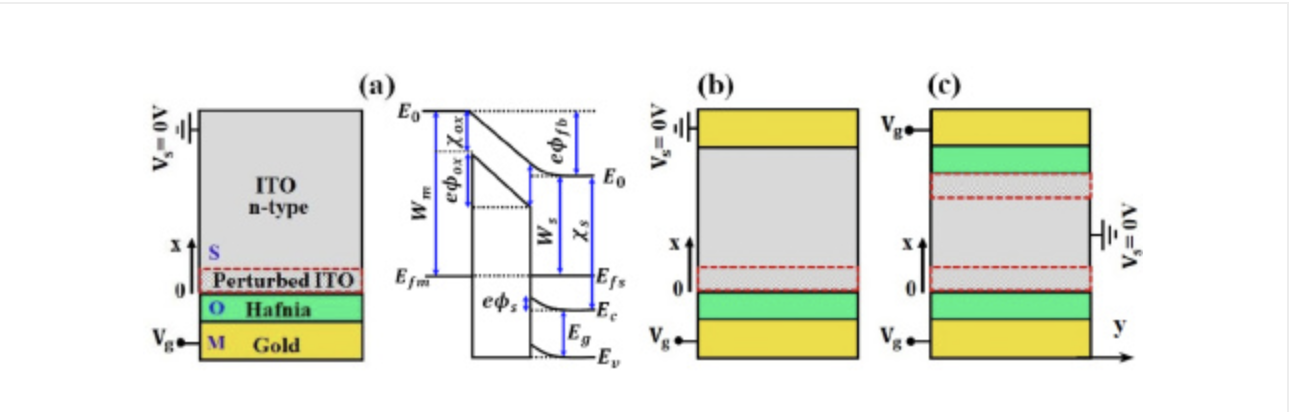
The carrier density profile in metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) capacitors is computed under gating using two classical models - conventional drift-diffusion (CDD) and density-gradient (DG) - and a self-consistent Schrödinger-Poisson (SP) quantum model.
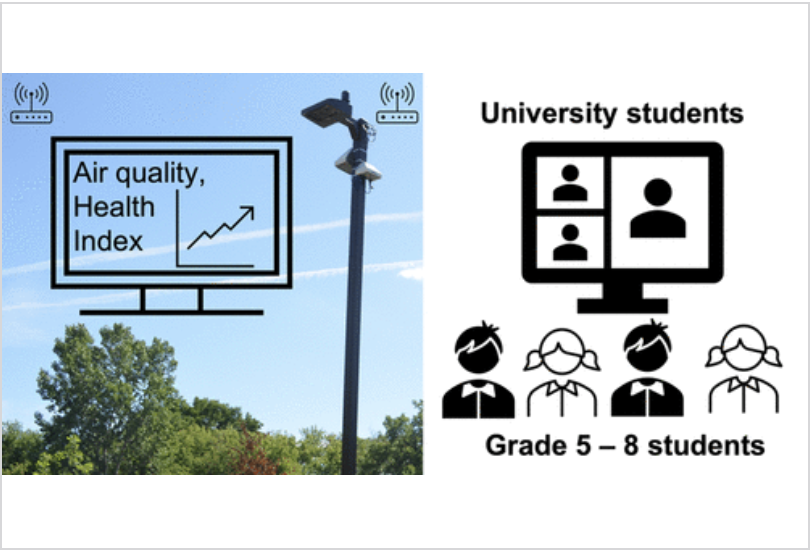
The City of Kitchener is the largest city in Waterloo Region in the province of Ontario, the third fasting growing region in Canada, yet it has only one air quality monitoring station. Our research group launched a pilot project in September 2020 to install a network of AQMesh multisensor mini air quality monitoring stations (pods) near elementary schools in Kitchener.
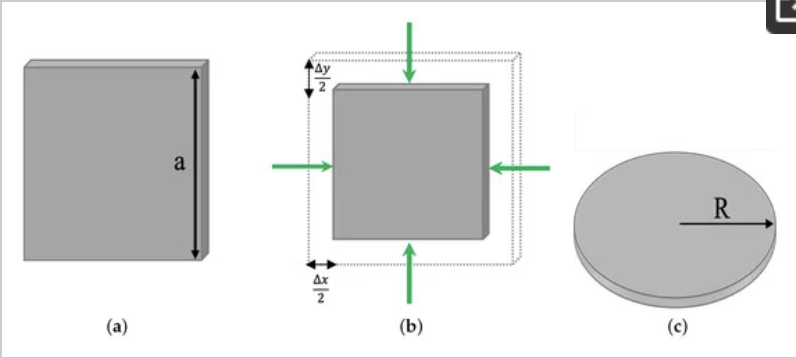
The trivial versus topological properties of the BHZ Hamiltonian are characterized by the different topologies that arise when mapping the in-plane wavevectors through the BHZ Hamiltonian onto a Bloch sphere. In the topologically nontrivial case, edge states are formed in the disc and square geometries of the quantum dot. We account for the effects of compressive strain in topological insulator quantum dots by means of the Bir–Pikus Hamiltonian.
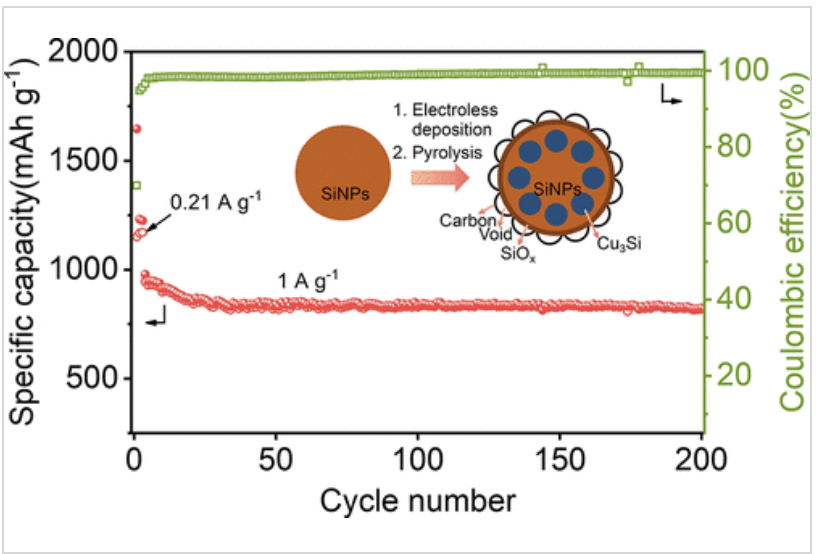
Silicon (Si), a promising anode material for lithium-ion batteries, usually suffers from low capacity retention and poor rate performance due to its huge volume change issue and low electronic conductivity.
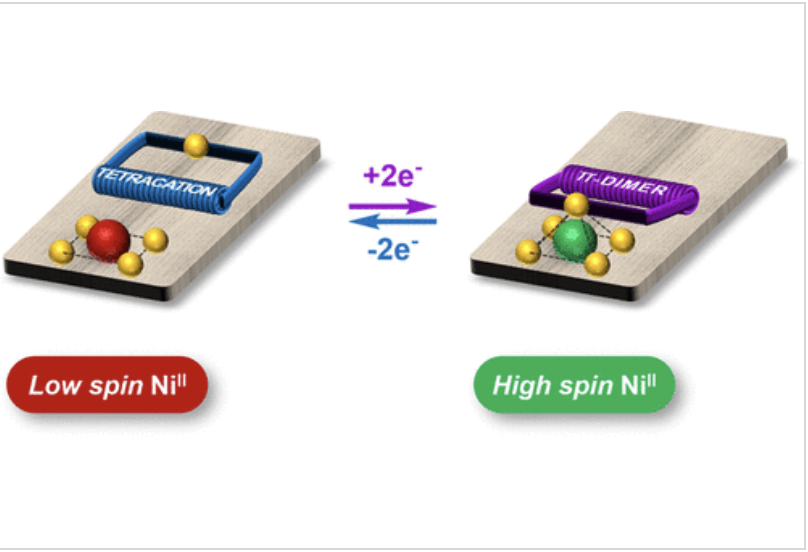
We herein report the synthesis and magnetic properties of a Ni(II)-porphyrin tethered to an imidazole ligand through a flexible electron-responsive mechanical hinge. The latter is capable of undergoing a large amplitude and fully reversible folding motion under the effect of electrical stimulation.
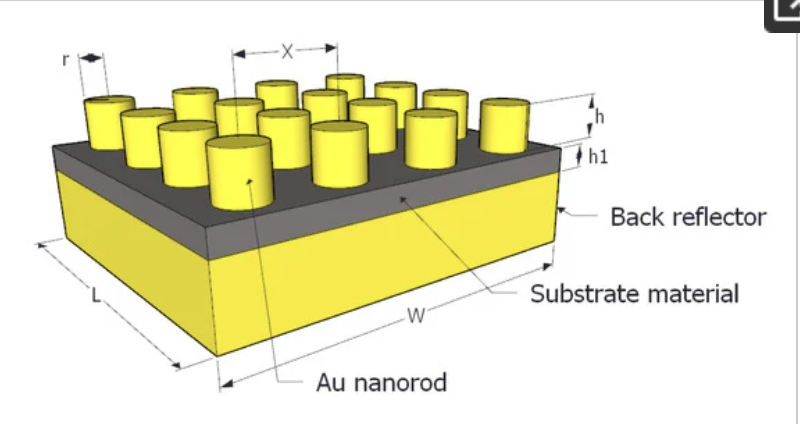
A broadband thin film plasmonic metamaterial absorber nanostructure that operates in the frequency range from 100 GHz to 1000 GHz is introduced and analyzed in this paper. The structure consists of three layers: a 200 nm thick gold layer that represents the ground plate (back reflector), a dielectric substrate, and an array of metallic nanorods. A parametric study is conducted to optimize the structure based on its absorption property using different materials
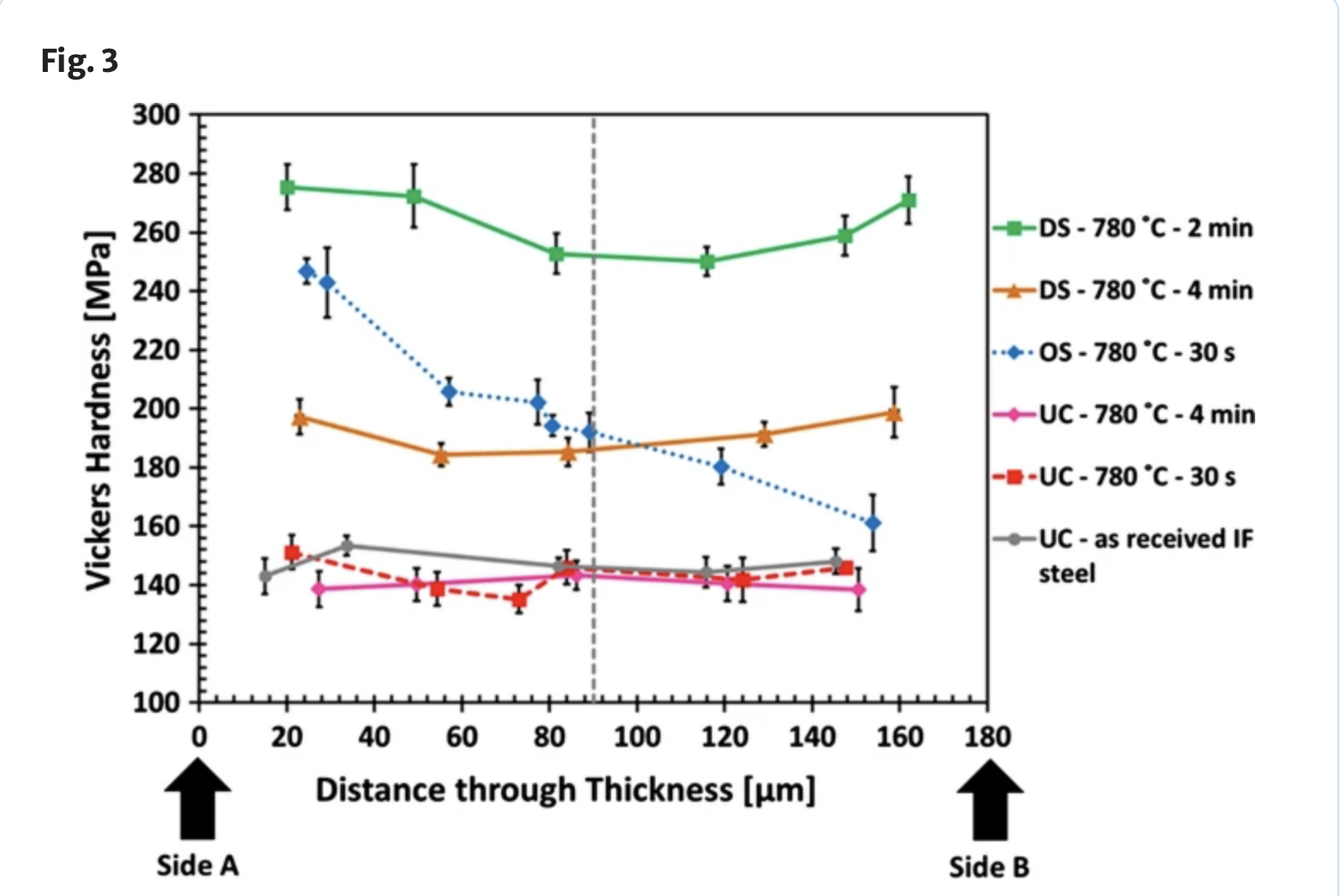
A new process to rapidly obtain high-strength interstitial free (IF) steel was investigated. Thin sheets of IF steel were coated on one or both sides with an amorphous FeC film and subjected to a two-step induction heating cycle (1100 °C followed by an isothermal hold at 780 °C for 2 or 4 min) and a rapid quench in water.
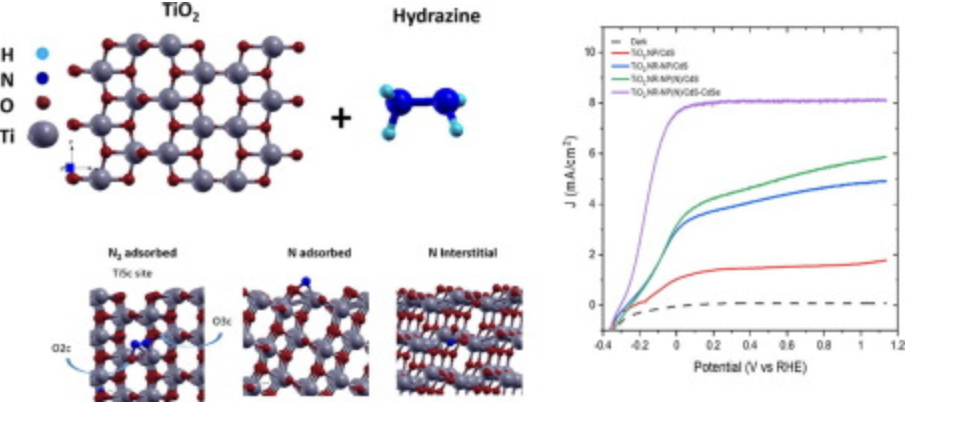
We report the synthesis of a TiO2 hybrid structure, consisting of a combination of nanorods and nanoparticles, subsequently treated with hydrazine to enhance the performance of photoelectrochemical (PEC) hydrogen (H2) generation. The optimized TiO2 hybrid photoanode sensitized with Quantum dots (QDs), yields a saturated photocurrent density of 4.25 mA cm−2 (at 0.8 V vs RHE), which is 172% higher than that of the reference sample.
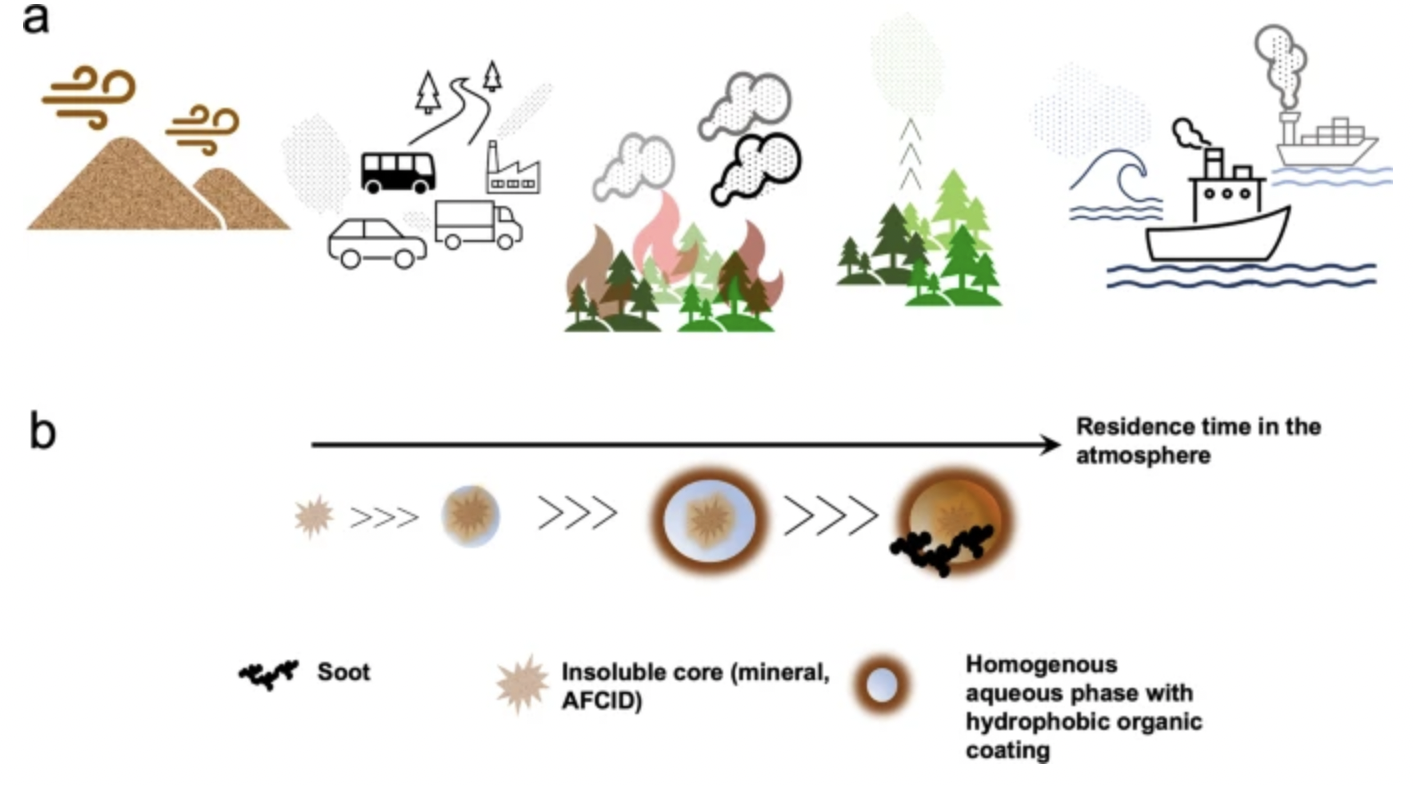
Transition metals are increasingly recognized as key drivers in the formation and aging of light-absorbing organic aerosols, known as brown carbon, which impact the energy flux in the atmosphere.
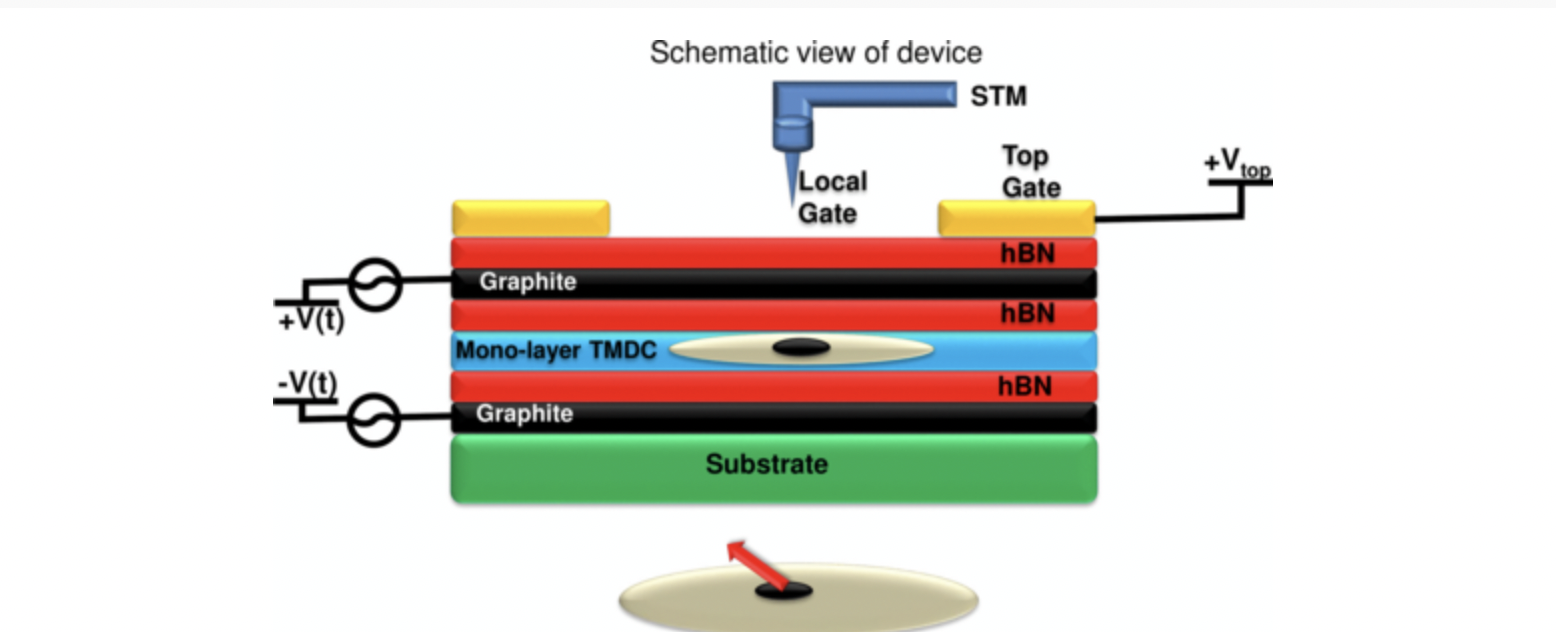
We develop a microscopic and atomistic theory of electron-spin-based qubits in gated quantum dots in a single layer of transition metal dichalcogenides. The qubits are identified with two degenerate locked spin and valley states in a gated quantum dot.
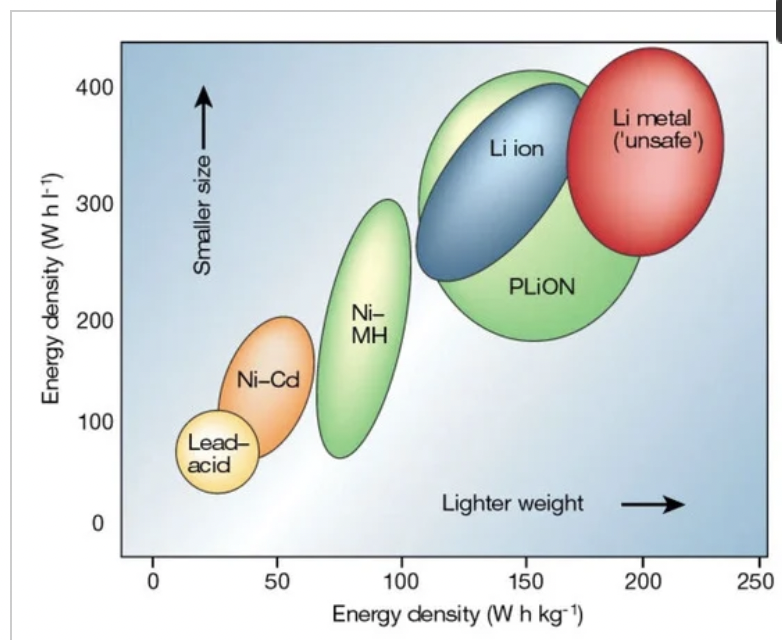
Solid-state lithium metal batteries (LMBs) have become increasingly important in recent years due to their potential to offer higher energy density and enhanced safety compared to conventional liquid electrolyte-based lithium-ion batteries (LIBs).
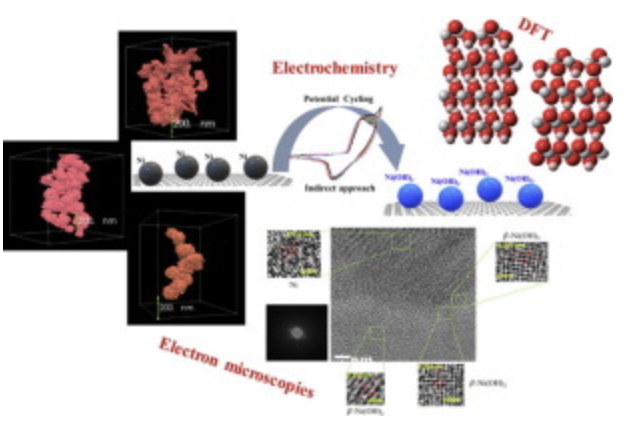
Shape-controlled microstructures (triangles and urchin-like) of Ni were synthesized using polyol synthesis in the presence/absence of capping agent (polyvinilpyrrolidone, PVP). Direct visualization of crystal structure and morphology before/after electrochemical tests in KOH were characterized using electron microscopy techniques.
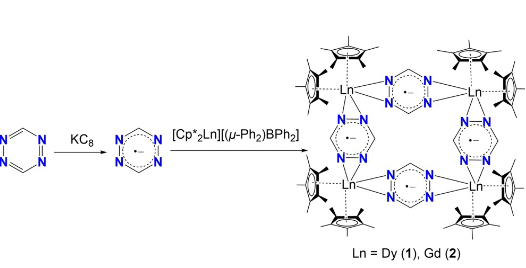
Inducing magnetic coupling between 4f elements is an ongoing challenge. To overcome this formidable difficulty, we incorporate highly delocalized tetrazinyl radicals, which strongly couple with f-block metallocenes to form discrete tetranuclear complexes.
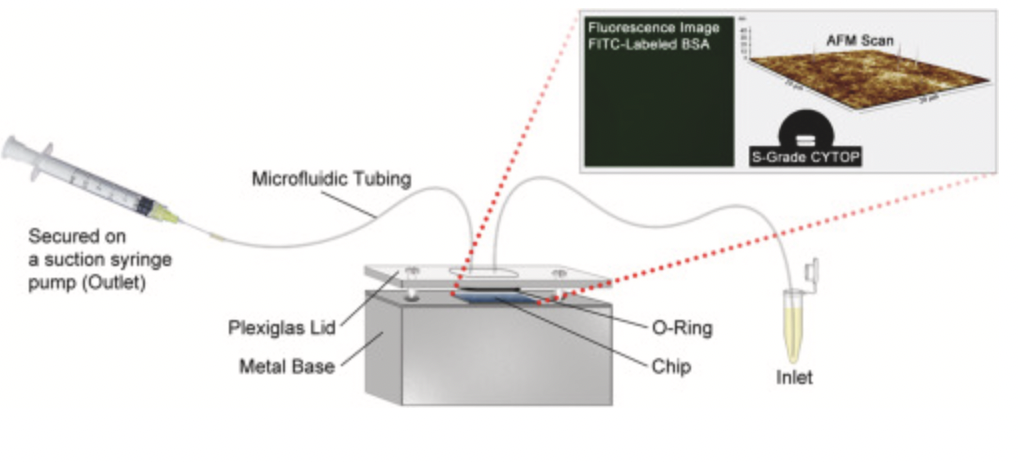
Non-specific adsorption proteins to the surfaces of microfluidics channels poses a serious problem in lab-on-a-chip devices involving complex biological fluids
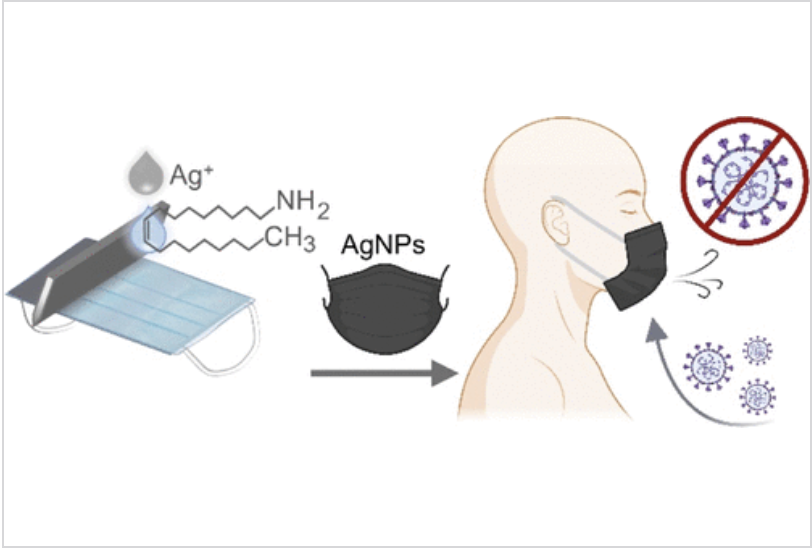
The Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) global outbreak and its continued growth and mutation into various forms emphasize the need for effective disinfectants to assist in the reduction of the virus’s spread from individual to individuals and community to communities through various modes, including coughing, sneezing, touching of contaminated surfaces, and being in proximity of an unprotected infected person, to mention a few.
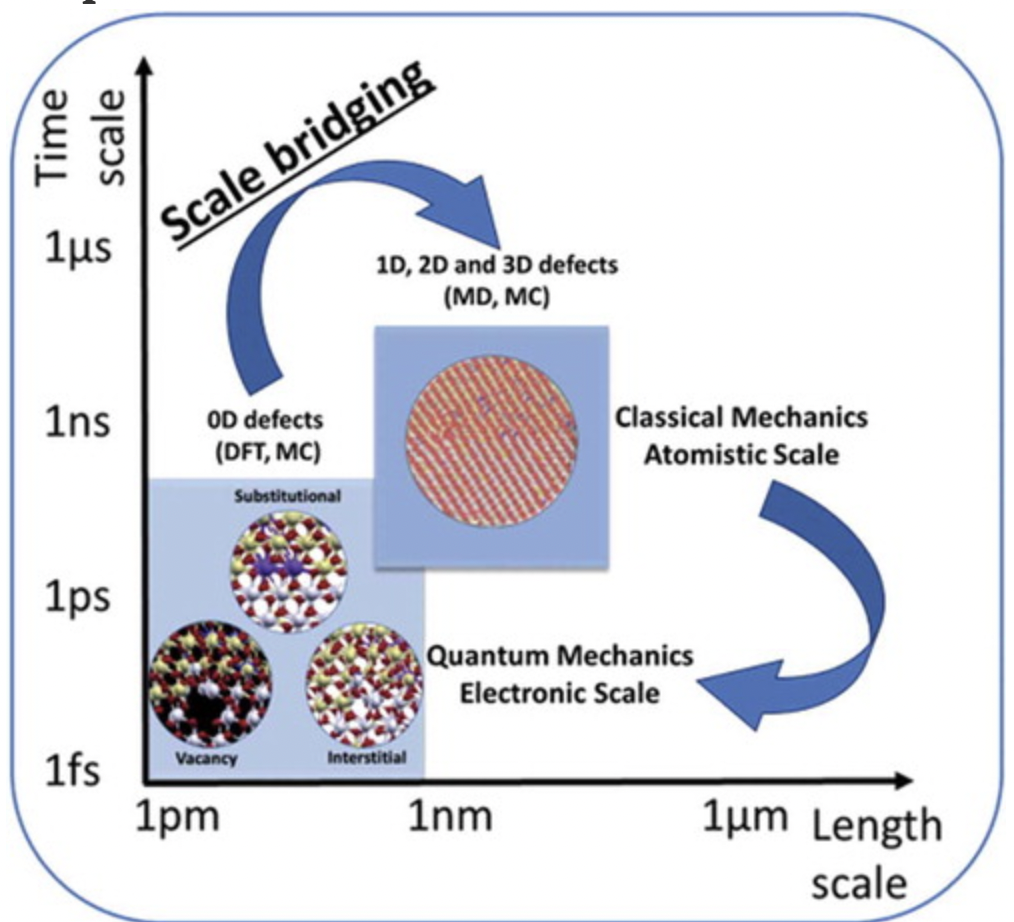
The functionality of the materials used for energy applications is critically determined by the physical properties of small active regions such as dopants, dislocations, interfaces, grain boundaries, etc.